Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Adult Syphilis: A Narrative Review of Clinical Insights and Public Health Implications in Urology
- Seung-Ju Lee, Jin Bong Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):123-131. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550039017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Syphilis continues to pose a major global public health concern, with more than 7 million cases reported worldwide in 2022, and its incidence continues to rise in numerous regions. In Korea, the shift from sentinel to universal notification in 2024 has revealed a markedly greater disease burden, particularly among men who have sex with men and among younger adults, underscoring changing epidemiological patterns and the urgent need for revised control strategies. In urological practice, syphilis presents with a wide range of often misleading symptoms, including painless genital ulcers, urethritis, and sexual dysfunction, that frequently resemble other genitourinary disorders and complicate diagnostic evaluation. Accurate identification relies on integrating a thorough clinical assessment with serologic testing while remaining alert to diagnostic challenges such as early latent infection, serofast states, and human immunodeficiency virus coinfection. Penicillin G remains the mainstay of therapy, with treatment regimens tailored to the stage of disease and to the presence or absence of central nervous system involvement. Effective partner notification, targeted screening, and consistent follow-up are essential to prevent reinfection and limit further transmission. At a public health level, a multifaceted strategy—strengthened surveillance systems, focused testing in high-risk populations, and embedding syphilis screening within broader sexually transmitted infection care frameworks—is critical to curbing its resurgence. In summary, prompt recognition, adherence to evidence-based management, and coordinated public health measures, together with ongoing advances in diagnostics and prevention, remain fundamental to reducing the continued spread of syphilis and mitigating its impact on both individual and population health.
- 322 View
- 7 Download

Case Report
- Primary Bladder and Ureteral Amyloidosis Initially Diagnosed as Chronic Cystitis: A Case Report
- Seungsoo Lee, Dan Bee Lee, Hyun Jung Lee, Won Hoon Song, Sung-Woo Park, Jong Kil Nam
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):167-172. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550038019
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Primary localized amyloidosis confined to the urinary tract is uncommon and frequently misinterpreted due to clinical and radiologic overlap with more prevalent conditions. We describe a 69-year-old woman who experienced recurrent gross hematuria over 2 years and underwent initial transurethral resection based on a presumptive diagnosis of chronic cystitis. Subsequent evaluation revealed a left ureteral mass with hydronephrosis, raising concern for malignancy. Histopathologic examination of both bladder and ureteral specimens demonstrated amorphous eosinophilic deposits that stained positive with Congo red and showed apple-green birefringence under polarized microscopy. Immunofluorescence confirmed λ-light-chain predominance, establishing AL (amyloid light chain)-type amyloidosis without systemic involvement. The patient underwent complete endoscopic resection and remains asymptomatic during ongoing surveillance. This case highlights the diagnostic challenges posed by localized urinary amyloidosis and underscores the importance of histologic confirmation in atypical inflammatory lesions.
- 315 View
- 4 Download

Original Article
- Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors of Fournier Gangrene: A 15-Years Multicenter Retrospective Study in Korea
- Seung-Kwon Choi, Sin Woo Lee, Hyung-Lae Lee, Jeong Woo Lee, Jung Sik Huh, Yeonjoo Kim, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):159-166. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550036018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose
Fournier gangrene (FG) is a rare but life-threatening necrotizing infection requiring prompt recognition and intervention. This multicenter study aimed to investigate the clinical characteristics, treatment outcomes including mortality, and risk factors associated with death among patients with FG over the past 15 years in Korea. Materials and Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 84 patients diagnosed with FG between 2008 and 2022 across 7 hospitals. Demographics, comorbidities, laboratory findings, and clinical outcomes were analyzed. Mortality-related risk factors were assessed using univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Results
The mean age was 58.1±15.9 years, and 95.2% of patients were male. Diabetes mellitus (42.9%) and hypertension (36.9%) were the most prevalent comorbidities. Sepsis developed in 38.1% of patients, and the overall mortality rate was 14.3%. In univariate analysis, age ≥70 years, low body mass index, diabetes mellitus, low hemoglobin, low hematocrit, high respiratory rate, and Fournier gangrene severity index (FGSI) ≥9 were significantly associated with mortality. After data correction and multivariate adjustment, diabetes mellitus (odds ratio [OR], 39.61; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.39–656.32; p=0.010) and respiratory rate (OR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.09–1.91; p=0.011) were identified as independent predictors of mortality. FGSI≥9 demonstrated borderline association with mortality (p=0.08), indicating its potential clinical relevance.
Conclusions
In this multicenter Korean cohort, the mortality rate of FG remained substantial at 14.3%. Diabetes mellitus and elevated respiratory rate were independent predictors of mortality, while FGSI≥9 demonstrated a borderline yet clinically meaningful association, suggesting its role as a useful severity indicator in early risk stratification.
- 247 View
- 9 Download

Review Articles
- Beyond the Number: Interpreting Prostate-Specific Antigen Elevation in the Context of Prostate Inflammation
- Byoungkyu Han, Ki-Hyuck Moon
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):132-143. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550032016
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) is indispensable but not cancer specific; inflammation, benign prostatic hyperplasia, urinary retention, ejaculation, and instrumentation can all elevate PSA and complicate cancer risk assessment. This review synthesizes current evidence and guidelines to support clinicians in interpreting PSA elevations when inflammation is present or suspected. Acute febrile urinary tract infection and acute bacterial prostatitis may produce very high PSA values, sometimes exceeding 100 ng/mL, and normalization can be slow; therefore, PSA testing during active infection is discouraged. When PSA is only mildly to moderately elevated, standardized repeat testing is essential because a meaningful proportion of results normalize on retesting. A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-first pathway improves detection of clinically significant prostate cancer while reducing overdiagnosis and enables biopsy deferral after a negative MRI under structured monitoring. PSA density (PSAD) further refines triage alongside MRI, with practical working thresholds of roughly 0.10–0.20 ng/mL/cm3 calibrated to MRI quality and pretest risk. However, asymptomatic histologic prostatitis (National Institutes of Health category IV) is common and may raise PSA without reliably altering PSAD, which means that PSAD alone cannot confirm that an elevation is attributable solely to inflammation. Validated secondary biomarkers (e.g., Prostate Health Index, 4Kscore, IsoPSA [isoform PSA], Stockholm3, Proclarix, PCA3 [prostate cancer gene 3], SelectMDx [select molecular diagnostics], ExoDx [exosome diagnostics], MPS/MPS2 [MyProstateScore/MyProstateScore 2.0]) are best used selectively when MRI is negative or equivocal and clinical risk remains uncertain. A pragmatic sequence—confirm, image, and refine—helps minimize missed clinically significant cancer while reducing unnecessary antibiotics and biopsies when inflammation is the predominant driver of PSA elevation.
- 386 View
- 13 Download

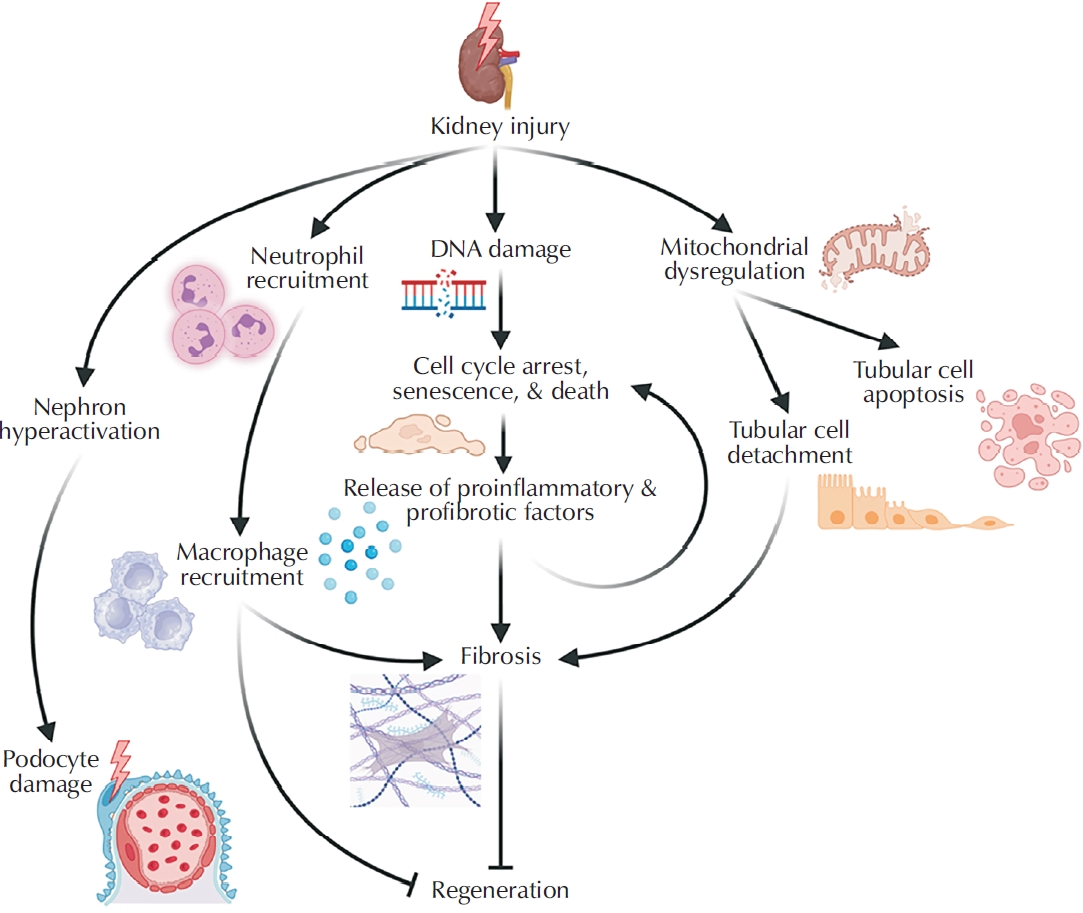
- Regenerative Medicine for the Kidney
- Vladimir Mashanov, Ji Hyun Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):144-158. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550028014
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Kidney disease poses a major and growing global health challenge, with both prevalence and mortality continuing to rise. Current standard-of-care treatments, including dialysis and kidney transplantation, have significant limitations and do not adequately meet clinical needs. This unmet need has driven the development of next-generation regenerative medicine strategies, which can be broadly categorized into 3 areas: (1) approaches that enhance the kidney’s limited intrinsic regenerative capacity; (2) stem cell-based therapies; and (3) implantable bioengineered kidney constructs. This review summarizes recent advances in each of these domains and discusses the major biological, technical, and regulatory challenges that must be addressed to enable successful clinical translation.
- 330 View
- 7 Download

Case Report
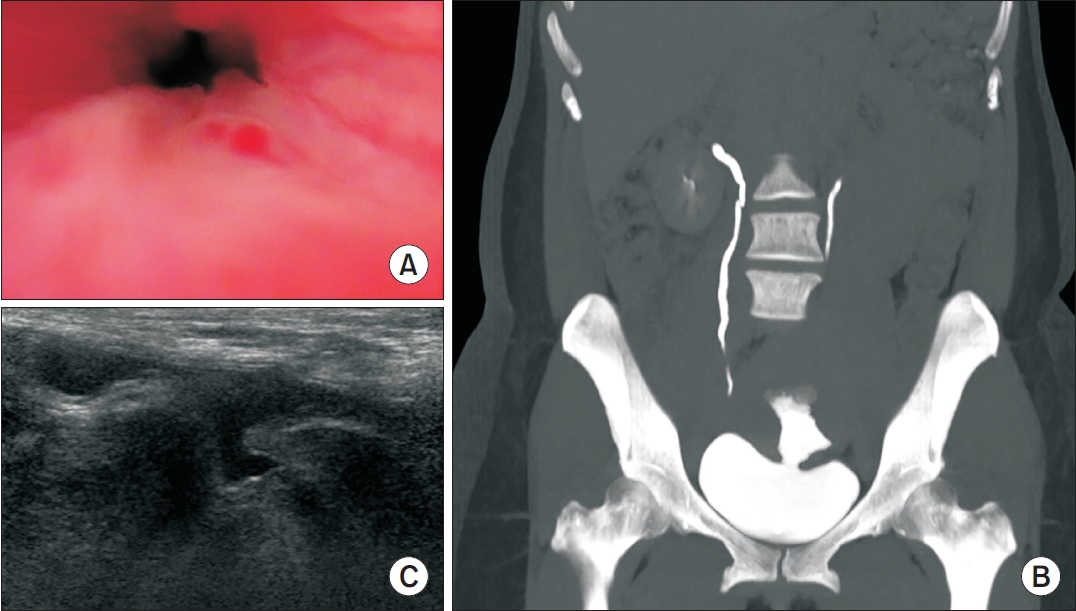
- Cyclic Hematuria Misdiagnosed as Hemorrhagic Cystitis in a Rare Case of Vesicouterine Fistula Post-Cesarean Section: A Case Report of Youssef Syndrome
- Youngjoo Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(2):114-117. Published online August 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550024012
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - Vesicouterine fistulas are rare complications that may occur following cesarean sections and are frequently misdiagnosed due to their diverse clinical presentations. This report presents a case involving a small vesicouterine fistula initially managed conservatively, which later manifested as cyclic hematuria mimicking hemorrhagic cystitis, ultimately leading to a diagnosis of Youssef syndrome. A 45-year-old woman developed persistent vaginal urinary leakage 3 weeks after a cesarean section. Diagnostic evaluation confirmed a small (<1 cm) vesicouterine fistula. Conservative management with Foley catheterization resulted in spontaneous closure. Four months later, the patient experienced cyclic gross hematuria and dysuria without menstruation, and was subsequently diagnosed with Youssef syndrome. Hormonal therapy using continuous oral contraceptives successfully resolved the hematuria, providing a noninvasive therapeutic option. This case highlights the importance of considering Youssef syndrome in patients with cyclic hematuria after cesarean section, in order to distinguish it from hemorrhagic cystitis and ensure timely, appropriate management.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(2): 55. CrossRef
- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 1,089 View
- 10 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
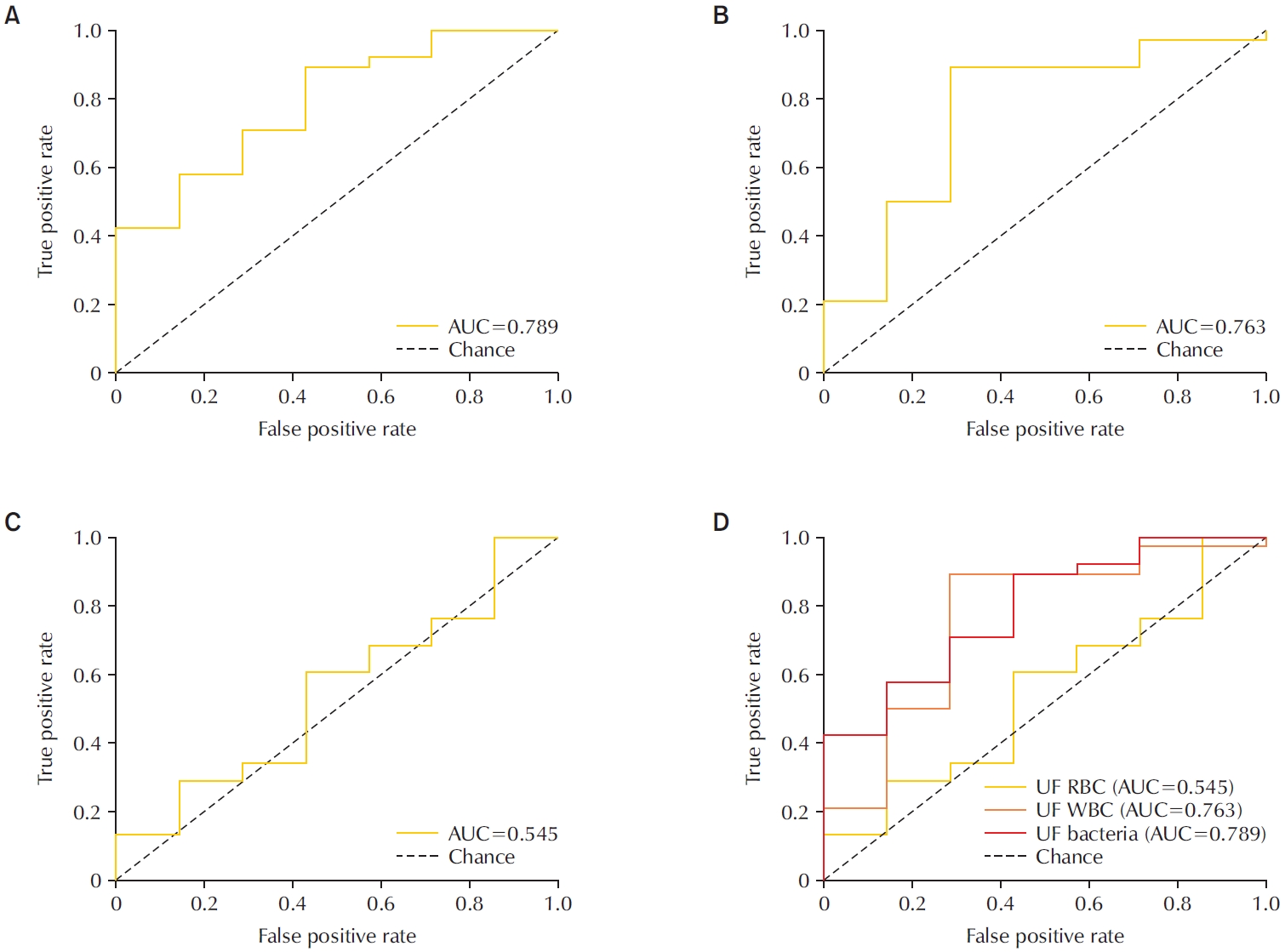
- Diagnostic Utility of the Sysmex UF-5000 Flow Cytometer in Acute Bacterial Prostatitis: A Retrospective Pilot Study
- Young Kyu Han, Jeong Woo Lee, Hae-Il Park, Jin Bong Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(2):107-113. Published online August 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550022011
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader - Purpose
To evaluate the diagnostic performance of the Sysmex UF-5000 flow cytometer in detecting acute bacterial prostatitis (ABP) compared to standard urine culture. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study analyzed 45 urine samples from patients with a clinical diagnosis of ABP. Each sample was evaluated using the UF-5000 to measure red blood cells (RBC), white blood cells (WBC), and bacterial counts, and the results were compared with those from standard urine culture and Gram staining. Receiver operating characteristic curves were generated, and sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value were determined. Concordance between Gram classification by the UF-5000 and conventional Gram staining was also evaluated.
Results
Of the 45 patients, 84.4% had positive urine cultures. The bacterial count parameter demonstrated the highest diagnostic performance (area under the curve [AUC]=0.79; sensitivity, 89.5%; PPV, 91.9%), outperforming WBC (AUC=0.76) and RBC (AUC=0.55). The Gram classification flag showed an overall concordance of 85.7% with conventional Gram staining, with a concordance rate of 88% for Gram-negative organisms.
Conclusions
The Sysmex UF-5000 exhibited good concordance with urine culture for patients with ABP, particularly through the bacterial count parameter. Although it does not replace culture, the UF-5000 may serve as a rapid adjunctive tool to support early clinical decision-making in suspected ABP cases. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(2): 55. CrossRef
- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 1,225 View
- 26 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Articles
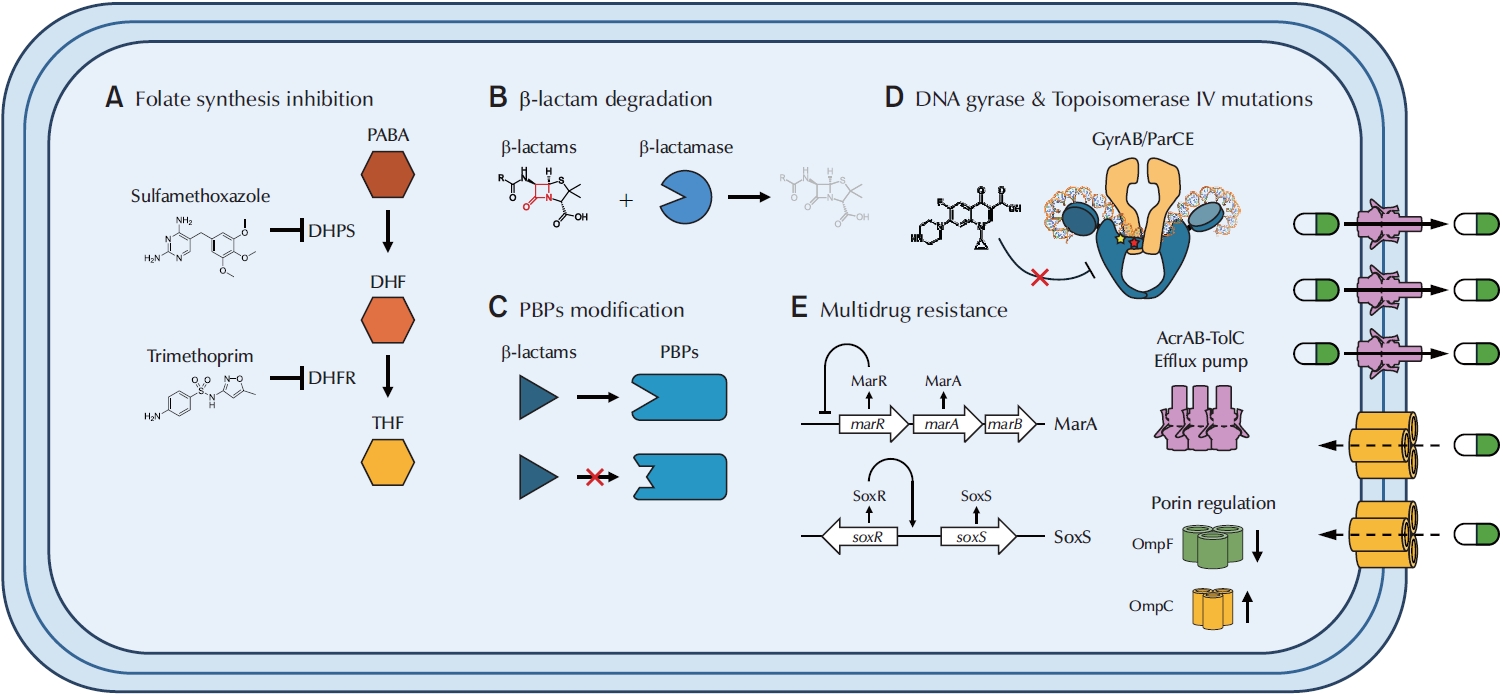
- Molecular Mechanisms of Antibiotic Resistance in Uropathogenic Escherichia coli: A Narrative Review
- Nakjun Choi, Dong Uk Kim, Eun-Jin Lee
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(2):96-106. Published online August 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550018009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most prevalent bacterial infections worldwide, with uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC) serving as the primary causative agent. Although antibiotic therapy remains the standard of care for UTI treatment, the increasing prevalence of antimicrobial resistance has substantially reduced the effectiveness of commonly prescribed antibiotics. Resistance to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX), β-lactams, and fluoroquinolones is particularly concerning, as these agents constitute the principal therapeutic options for UTIs. This review examines the molecular mechanisms underlying UPEC resistance to these three classes of antibiotics, including target site modifications, efflux pump overexpression, porin regulation, and enzymatic degradation. Furthermore, it explores how these resistance determinants contribute to the development of multidrug-resistant (MDR) UPEC strains, which demonstrate cross-resistance to multiple antibiotics and present significant challenges for clinical management. Novel therapeutic strategies, such as efflux pump inhibitors, bacteriophage therapy, and genomic-guided precision medicine, are under investigation as potential solutions to address the growing global burden of MDR UPEC, alongside alternative non-antibiotic treatments. This review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the genetic and regulatory pathways driving antibiotic resistance in UPEC, offering insights that may guide the development of effective treatment strategies and help mitigate the ongoing spread of antimicrobial resistance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(2): 55. CrossRef
- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 5,328 View
- 87 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The Role of the Urinary Microbiome in the Prevention of Pediatric Urinary Tract Infections: A Narrative Review
- Byeongdo Song
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(2):82-95. Published online August 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550016008
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are a common condition in children and often lead to hospitalization. A considerable proportion of children with UTIs (up to 30%) experience at least one recurrence, placing them at risk for long-term complications such as renal scarring. Since the concept of the microbiome was first introduced in 2001, increasing attention has been given to the role of the urinary tract microbiome in maintaining urinary tract homeostasis. Dysbiosis of the urinary microbiome has been recognized as a factor associated with an increased risk of various urinary tract diseases, including UTIs. However, the specific role of the urinary microbiome in the pathophysiology of pediatric UTIs remains incompletely understood. The present review examines recent studies on the urinary microbiome in children and summarizes current strategies for modulating the urinary microbiome to prevent UTI recurrence in the pediatric population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(2): 55. CrossRef
- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 3,622 View
- 48 Download
- 1 Crossref

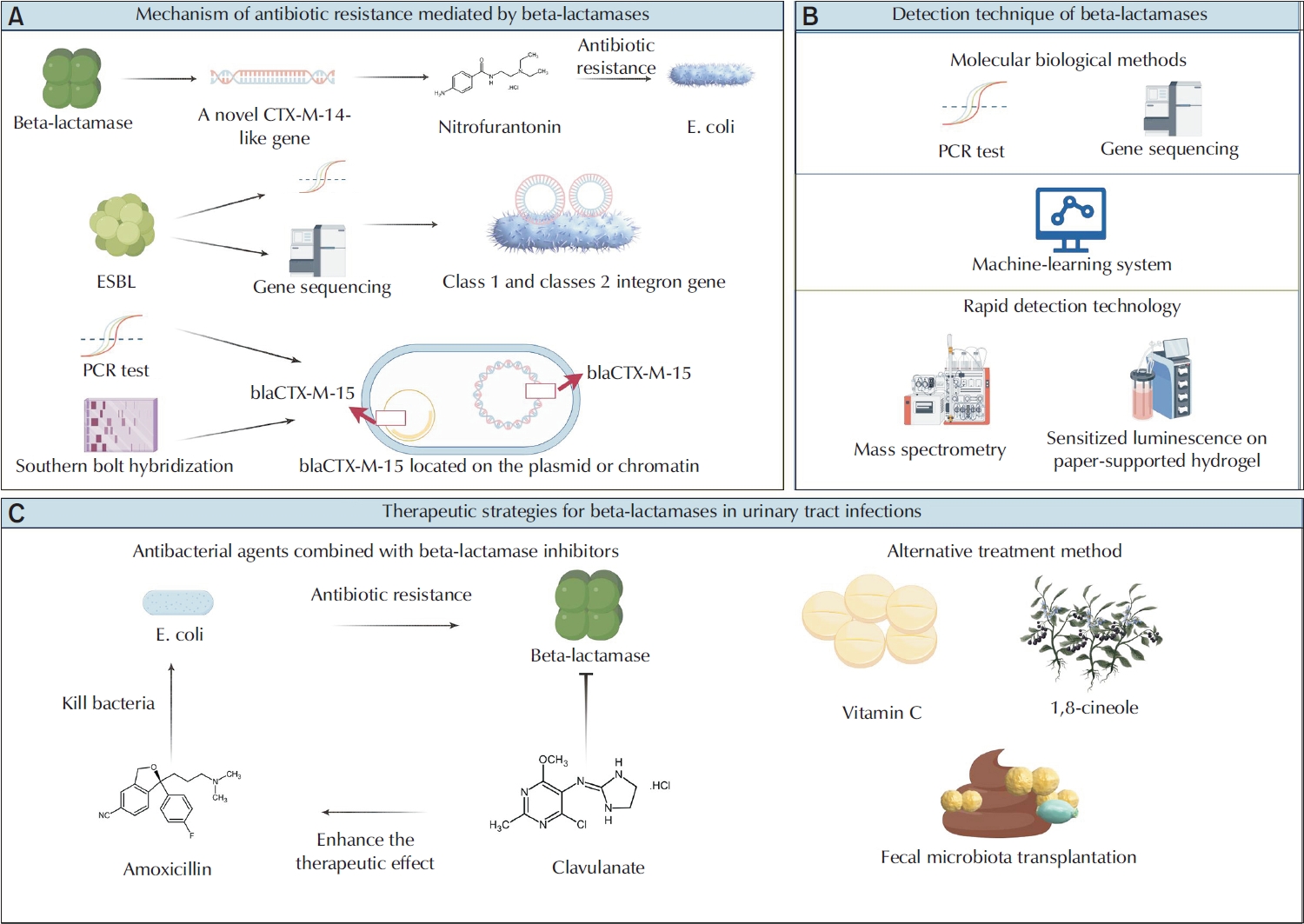
- Beta-Lactamase-Mediated Antibiotic Resistance in Urinary Tract Infections: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies
- Fanglin Shao, Dengxiong Li, Jie Wang, Zhouting Tuo, Zhipeng Wang, Wuran Wei, Ruicheng Wu, Dechao Feng
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(2):67-81. Published online August 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550012006
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most prevalent bacterial infections globally, and are primarily caused by Escherichia and Klebsiella. The overprescription and inappropriate use of antibiotics have accelerated the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria. Beta-lactamases play a critical role in mediating antibiotic resistance in UTIs. These enzymes promote bacterial resistance through multiple mechanisms, including gene mutation, plasmid-mediated horizontal gene transfer, and the involvement of integrons. Comprehensive knowledge of the ways in which beta-lactamases contribute to resistance in UTIs is essential for improving treatment strategies. Advances in detection technologies, such as gene sequencing and mass spectrometry, have greatly enhanced the ability to monitor and predict bacterial resistance. Current therapeutic strategies include the application of beta-lactamase inhibitors, the development of novel antibiotics, and alternative treatments that have shown efficacy against beta-lactamase-mediated antibiotic resistance. This paper reviews the mechanisms of beta-lactamase-mediated resistance in UTIs and provides an in-depth overview of several detection methods and therapeutic approaches.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(2): 55. CrossRef
- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 5,608 View
- 68 Download
- 1 Crossref

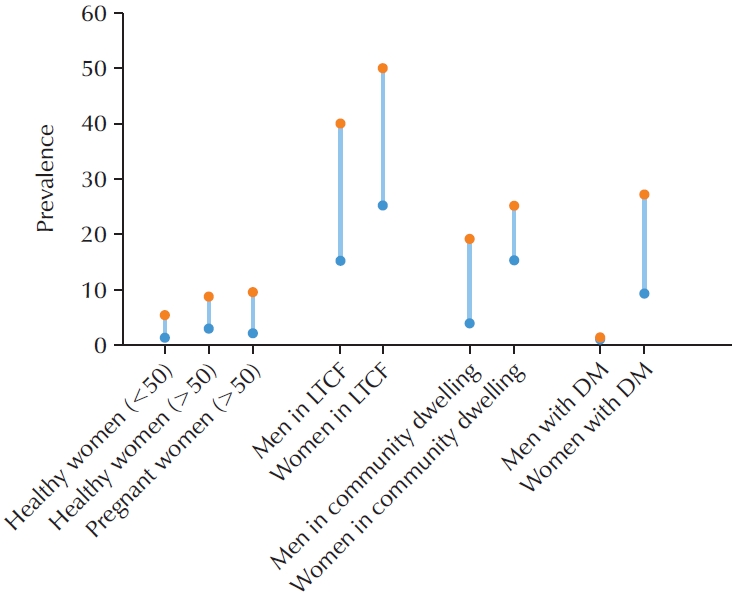
- Asymptomatic Bacteriuria in Older Adults – Diagnosis, Management, and Future Directions: A Narrative Review
- Ki Hong Kim, Hee Jo Yang
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(2):58-66. Published online August 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550002001
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader - Asymptomatic bacteriuria (ASB) is defined as the presence of bacteria in the urine in the absence of urinary tract infection (UTI) symptoms. The prevalence of ASB increases with advancing age, particularly among older patients with underlying health conditions. ASB is especially common among residents of long-term care facilities; however, distinguishing ASB from symptomatic UTI in this population remains a significant clinical challenge. The frequent occurrence of ASB often results in unnecessary antibiotic administration, thereby contributing to the development of antibiotic resistance. Current clinical guidelines recommend screening for and treating ASB only in certain circumstances, such as prior to urological procedures or in pregnant women. There is a pressing need for improved diagnostic approaches to differentiate ASB more accurately from UTI, particularly in older adults. Reducing unnecessary urine testing and inappropriate antibiotic use may help prevent over-treatment and minimize associated risks, including Clostridium difficile infection and increased antimicrobial resistance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(2): 55. CrossRef
- Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 9,452 View
- 80 Download
- 1 Crossref

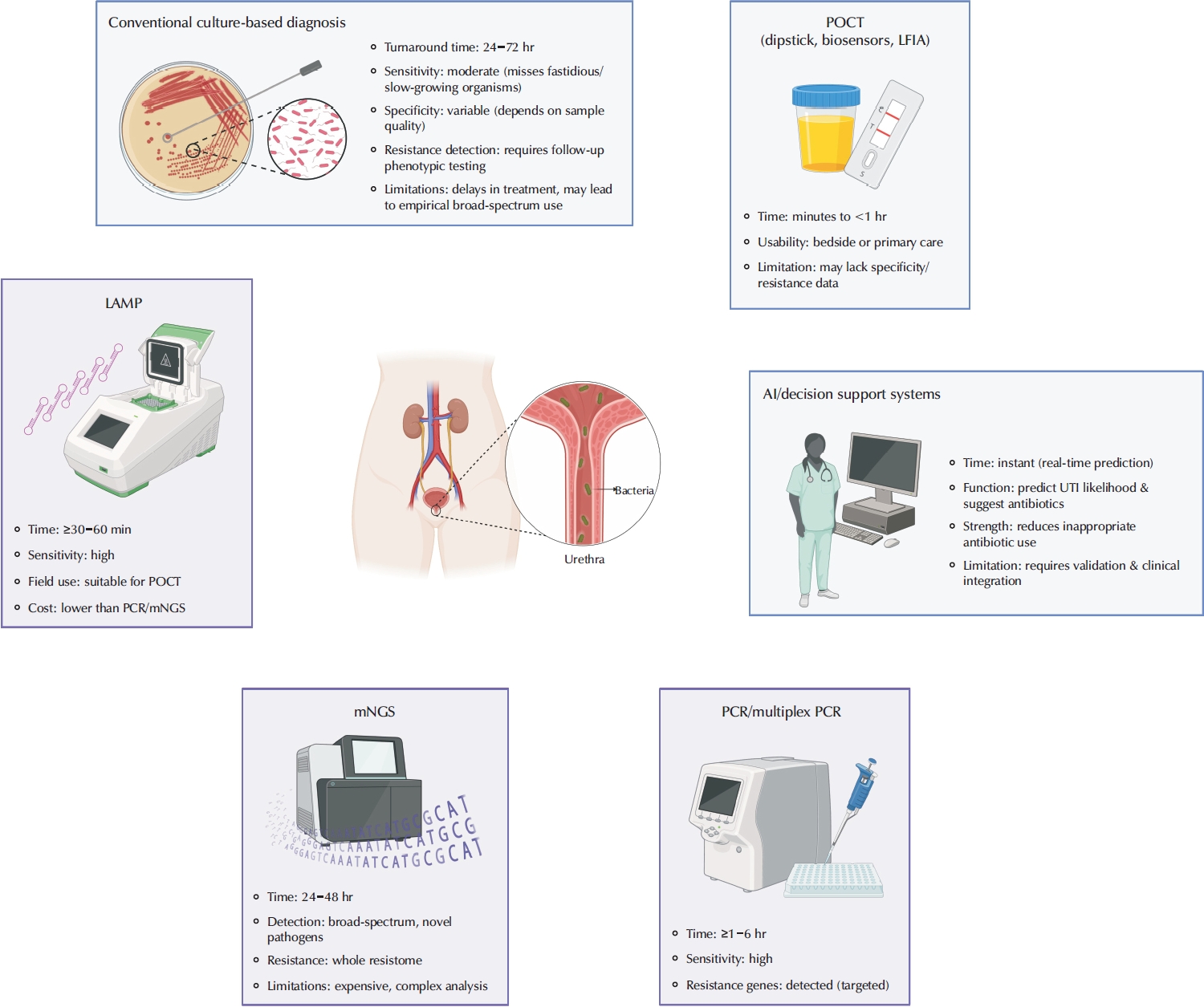
- Advances in the Diagnosis of Urinary Tract Infection: A Narrative Review
- Juan Victor Ariel Franco, Nicolás Meza
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):17-27. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550020010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Urinary tract infections are among the most frequent bacterial infections, significantly impacting patient morbidity and healthcare resources. Prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial to ensure effective treatment, prevent complications such as pyelonephritis or sepsis, and reduce inappropriate antibiotic use, contributing to antimicrobial resistance (AMR). Despite consensus across international guidelines from organizations, challenges persist, particularly in distinguishing true infections from asymptomatic bacteriuria or nonspecific symptoms, especially in older adults. Recent advancements in diagnostic technology have emerged to address these limitations, including molecular diagnostics, point-of-care testing (POCT), and artificial intelligence (AI)-driven predictive models. Molecular techniques, notably polymerase chain reaction, loop-mediated isothermal amplification, and metagenomic next-generation sequencing, offer enhanced sensitivity and specificity, rapid detection times, and comprehensive identification of pathogens and resistance profiles. POCT innovations, such as lateral flow immunoassays, enzymatic-based rapid tests, and novel biosensors, facilitate prompt bedside diagnosis, although specificity challenges remain. Meanwhile, AI and machine learning models demonstrate significant potential for risk stratification, prediction of infection, and improving antibiotics prescription practices yet face barriers related to validation, practical integration, and clinical acceptability. Despite promising developments, significant gaps remain, including limited real-world implementation evidence, high costs, and insufficient data from diverse populations. Further rigorous clinical studies, economic evaluations, and practical implementation assessments are urgently required. Addressing these research gaps could substantially improve patient outcomes, optimize antibiotic stewardship, and reduce the global burden of AMR.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diagnosis of urinary tract infections in the pediatric population – current practices, advances and progress
Maria Bitsori, Roza-Ioanna Poulaki, Emmanouil Galanakis
Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy.2026; : 1. CrossRef - Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef
- Diagnosis of urinary tract infections in the pediatric population – current practices, advances and progress
- 9,554 View
- 278 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Article
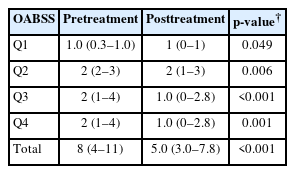
- Efficacy of Urovaxom for Improving Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome Symptoms in Prostate Cancer Patients Who Underwent Radical Prostatectomy: A Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Study
- Jun-Koo Kang, Yun-Sok Ha, Sungchan Park, Tae Gyun Kwon, Tae-Hwan Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):42-47. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550014007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS) is a multifactorial condition that can significantly diminish quality of life. Although some patients have reported persistent pelvic pain after radical prostatectomy (RP), the prevalence and direct causal relationship between CPPS and RP remain unclear. This multicenter prospective study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of Urovaxom for improving CPPS symptoms. Materials and Methods: A total of 52 prostate cancer patients who underwent RP were enrolled and administered Urovaxom (60 mg/day) for 12 weeks. Changes in National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI), overactive bladder symptom score (OABSS), International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), and inflammation markers (white blood cell [WBC], C-reactive protein [CRP]) were analyzed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Results
After 12 weeks of treatment, the NIH-CPSI total score significantly decreased from 19 (interquartile range [IQR], 16–23) to 12.5 (IQR, 8.0–16.8) (p<0.001). The OABSS total score decreased from 8 (IQR, 4–11) to 5 (IQR, 3.0–7.8), and the IPSS total score decreased from 13.5 (IQR, 10.0–22.8) to 10.5 (IQR, 5.0–17.0) (p<0.001). WBC levels showed a slight increase (p=0.028), but the clinical relevance of this change is uncertain and warrants further investigation. CRP changes were not statistically significant (p=0.274).
Conclusions
Urovaxom demonstrated significant efficacy in improving CPPS symptoms, particularly pain and reduced quality of life, in patients following RP. These findings suggest Urovaxom as a potential therapeutic option for CPPS after management using RP. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef - Addressing an Unmet Need in Postprostatectomy Care: Perspectives on Urovaxom
Byeong Jin Kang
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(2): 118. CrossRef
- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 4,760 View
- 42 Download
- 2 Crossref

Case Report
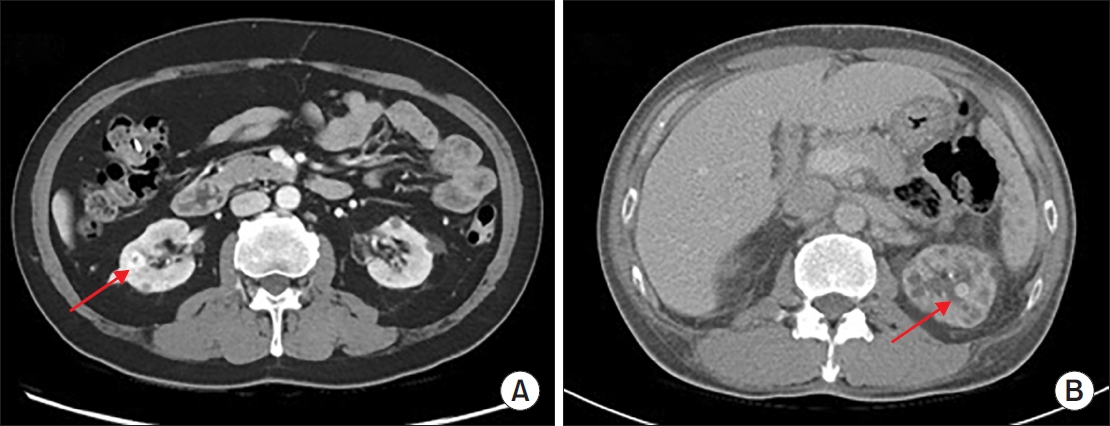
- Hemangioma Mistaken for Renal Cell Carcinoma in a Patient With End-Stage Renal Disease: A Case Report
- Hyung-Lae Lee, Dong-Gi Lee, Jeong Woo Lee, Jeonghyouk Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):48-51. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550008004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Hemangiomas are rare, benign vascular neoplasms that are more common in patients with end-stage renal disease. Here, we describe 2 cases of hemangioma misdiagnosed as renal cell carcinoma before renal transplantation. The key finding in our case was the misdiagnosis of hemangiomas as renal cell carcinoma based on computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in patients with end-stage renal disease. Because living transplantation was planned for our patients, we performed rapid surgical resection of the heterogeneously enhancing renal masses to avoid delays in transplantation. Our case highlights the importance of rapid surgical resection of enhanced renal masses to confirm diagnosis, thereby avoiding delays in patients scheduled for renal transplantation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef
- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 1,815 View
- 18 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
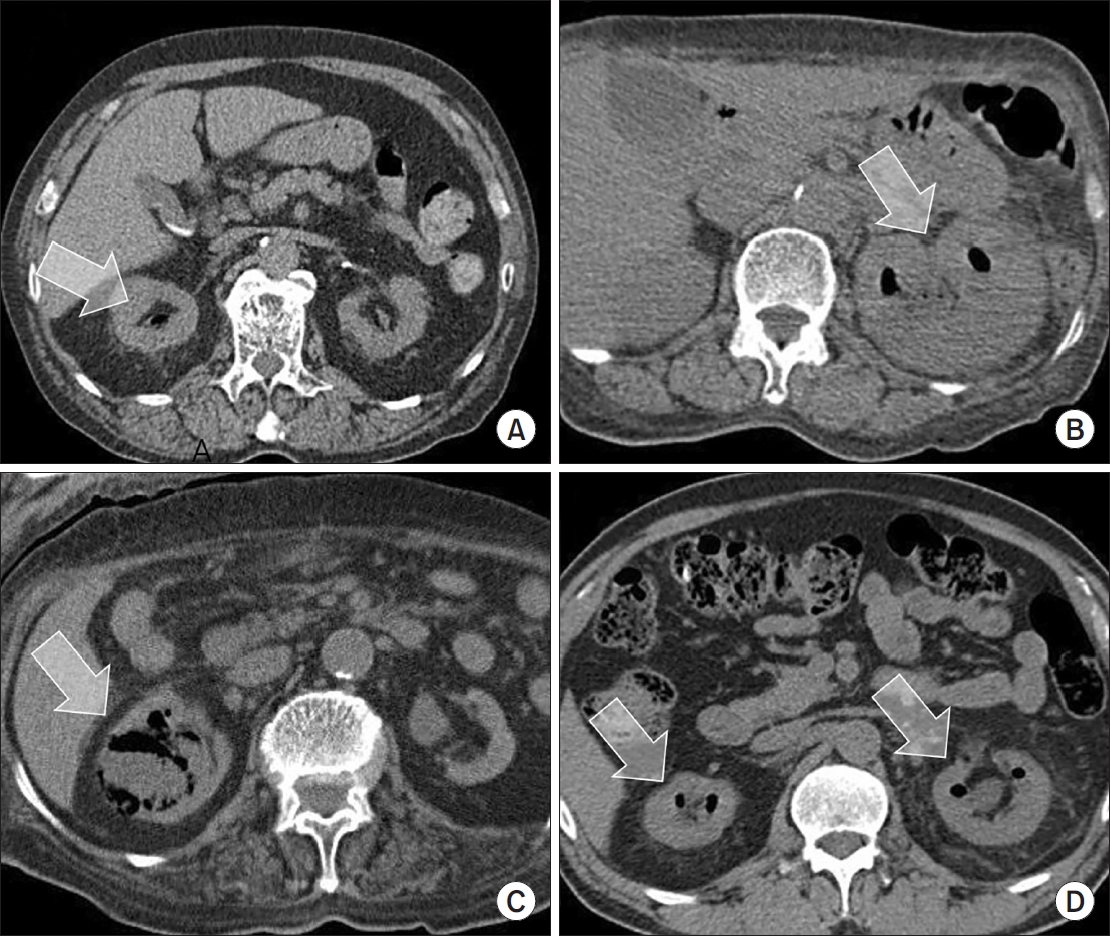
- Mortality and Risk Factors for Emphysematous Pyelonephritis in Korea: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study
- Seung-Kwon Choi, Jeong Woo Lee, Seung Il Jung, Eu Chang Hwang, Joongwon Choi, Woong Bin Kim, Jung Sik Huh, Jin Bong Choi, Yeonjoo Kim, Jae Min Chung, Ju-Hyun Shin, Jae Hung Jung, Hong Chung, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):34-41. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550006003
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose
Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) is a life-threatening disease requiring immediate treatment. This multicenter retrospective cohort study aimed to analyze the mortality rate and risk factors associated with EPN. Materials and Methods: Between January 2011 and February 2021, 217 patients diagnosed with EPN via computed tomography who visited 14 teaching hospitals were retrospectively analyzed. Clinical data, including age, sex, comorbidities, Huang and Tseng classification, hydronephrosis, acute kidney injury, blood and urine tests, surgical interventions, percutaneous drainage, and conservative treatments, were compared between the survival and death groups. Risk factors for mortality due to EPN were analyzed using univariate and multivariate methods.
Results
The mean age of survivors and deceased patients was 67.8 and 69.0 years, respectively (p=0.136). The sex distribution (male/female) was 48/146 and 8/15, respectively (p=0.298). Of the 217 patients, 23 died, resulting in a mortality rate of 10.6%. In univariate analysis, the Huang and Tseng classification (p=0.004), platelet count (p=0.005), and acute kidney injury (p=0.007) were significantly associated with mortality from EPN. In multivariate analysis, only the Huang and Tseng classification (p=0.029) was identified as a risk factor. Mortality rates according to the Huang and Tseng classification were as follows: class I (5.88%), class II (7.50%), class IIIa (14.28%), class IIIb (25.00%), and class IV (23.07%).
Conclusions
EPN is associated with a high mortality rate. Among various clinical factors, the Huang and Tseng classification was the most significant indicator for predicting mortality. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef
- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 3,118 View
- 59 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Articles
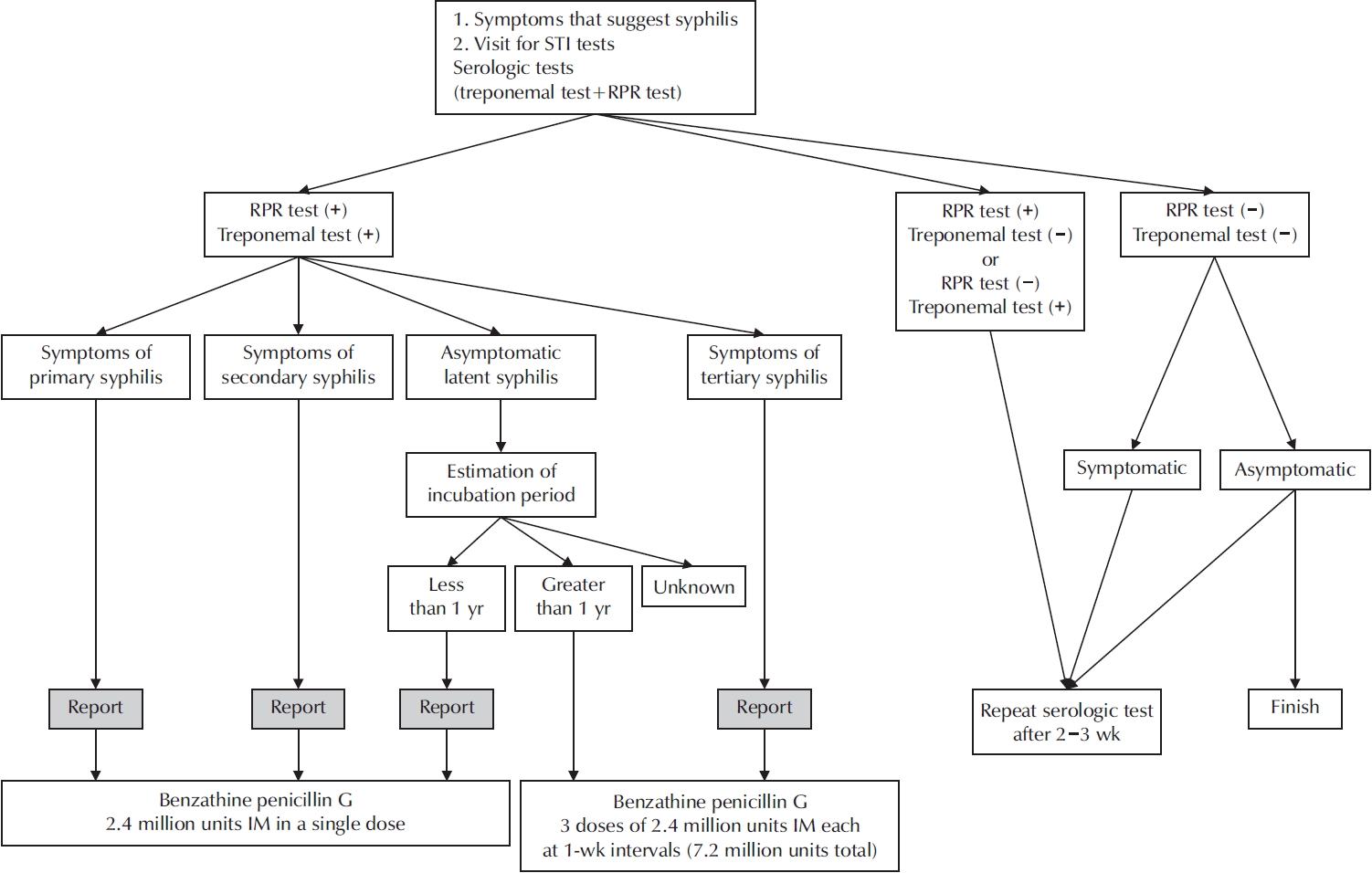
- A Narrative Review of Syphilis Notification Systems in Korea: Change to Mandatory Surveillance System
- Seung-Ju Lee, Jin Bong Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):28-33. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550004002
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
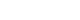
ePub - New cases of syphilis are clearly showing an increasing trend worldwide. However, in a sentinel surveillance system, the collection of information on disease outbreaks is limited, making it difficult to understand the overall outbreak situation and perform detailed analyses of patients' demographic characteristics and disease stages. In accordance with the revision of the Infectious Disease Prevention Act, syphilis was converted from a grade 4 infectious disease subject to sentinel surveillance to a grade 3 infectious disease subject to mandatory surveillance from January 1, 2024, with all medical institutions required to report syphilis diagnosis within 24 hours.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef - Adult Syphilis: A Narrative Review of Clinical Insights and Public Health Implications in Urology
Seung-Ju Lee, Jin Bong Choi
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(3): 123. CrossRef
- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 4,987 View
- 35 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Emerging Insights Into Microbiome Therapeutics for Urinary Tract Infections: A Narrative Review
- Hoonhee Seo, Md Abdur Rahim, Indrajeet Barman, Mohammed Solayman Hossain, Hanieh Tajdozian, Fatemeh Ghorbanian, Md Sarower Hossen Shuvo, Jiho Choi, Sukyung Kim, Heejo Yang, Ho-Yeon Song
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):4-16. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2448034017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most common bacterial infections worldwide, affecting millions annually and posing a significant global health concern. Traditional therapies for UTIs are becoming increasingly ineffective due to rising drug resistance and their tendency to disrupt the host's healthy microbiota, leading to further side effects. Consequently, there is an urgent need to develop alternative therapeutic agents that differ from conventional regimens and have fewer or no side effects. In this context, microbiome therapeutics offer a promising solution, given their demonstrated efficacy against various infectious diseases. Advances in scientific technology, particularly next-generation sequencing, have deepened our understanding of urinary microbiome dynamics, revealing a complex interplay within the urobiome that influences the onset and progression of UTIs. Uropathogenic bacteria do not solely cause UTIs; shifts in the composition of the urinary microbiome and interactions within the microbial community, known as host-microbiota interactions, also play a significant role. Although recent studies underscore the potential of targeting the urinary microbiome to manage UTIs and related complications, this field is still emerging and faces numerous regulatory and technical challenges. Further in-depth and comprehensive research is required to advance this pioneering concept into clinical practice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of N-acetylcysteine vs. probiotics in in-vivo biofilm prevention on ureteral stents: a prospective randomized controlled pilot in vivo study
Iqbal Singh, Himanshu Agrawal, Shailender Maurya, Himanshu Tanwar, Sanjay Gupta, N. P. Singh
International Urology and Nephrology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 13,544 View
- 155 Download
- 2 Crossref

- The Necessity of Human Papillomavirus Vaccination in Men: A Narrative Review
- Sooyoun Kim, Sangrak Bae
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(3):51-59. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2448030015
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Anogenital wart caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted infection. High-risk strains, such as types 16 and 18, cause penile cancer in men, cervical and vulvar cancers in women, and head and neck cancers and anal cancer in both sexes. Since these malignant tumors can be prevented through vaccination, the importance of vaccination is emphasized. However, because HPV is known to cause cervical cancer, vaccination is only being administered to women. Some countries vaccinate men as well, but in South Korea, only girls are included in the National Immunization Program. However, screening for HPV in men is not possible, and the virus causes various malignant tumors, with a sharp increase in head and neck cancers, as well as a surge in genital warts in the country. In addition, HPV worsens sperm quality. Moreover, the need for vaccines is increasing as the known methods for preventing HPV-related diseases in men are decreasing and the disease burden is increasing. As cost-effectiveness studies have shown that the cost-effectiveness of vaccination is lower for men than for women, it is unlikely that male vaccination will be included in national immunization programs. Many countries overseas, especially a very small number of OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) countries including South Korea, are implementing mandatory vaccination for women. Vaccinating men and women, would be cost-effective and efficient in achieving herd immunity. In addition to herd immunity, the inclusion of male vaccination in the National Immunization Program is imperative given the rapidly increasing incidence of diseases in men.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of sexually transmitted infections among persons aged 15–24 in Republic of Korea: A retrospective population-based descriptive study
Jinhee Seo, Minji Han, Sangrak Bae, Sooyoun Kim
Investigative and Clinical Urology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Human Papillomavirus Infection and Vaccine Uptake Among Males in the United Arab Emirates and the Wider Middle East and North Africa Region: A Narrative Review
Humaid AlKaabi, Raya Abu-Khalaf, Sandra Abu-Khalaf, Layan Abu-Khalaf, Yahia Khalil
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Prevalence of sexually transmitted infections among persons aged 15–24 in Republic of Korea: A retrospective population-based descriptive study
- 10,826 View
- 107 Download
- 2 Crossref

Original Article
- Outbreak of Cystoscopy-Related Urinary Tract Infections With Pseudomonas aeruginosa in South Korea, 2022: A Case Series
- Beomsoo Kim, Young-Sin Choi, Jun-Koo Kang, Yun-Sok Ha, Seock Hwan Choi, Bum Soo Kim, Hyun Tae Kim, Eun Sang Yoo, Tae Gyun Kwon, Jae-Wook Chung, Tae-Hwan Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(3):97-103. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2448028014
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose
This study conducted an epidemiological investigation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa urinary tract infections (UTIs) following cystoscopy at Chilgok Kyungpook National University Hospital. Materials and Methods: From May 16 to July 15, 2022, among 353 patients who underwent cystoscopy, 6 patients reported febrile UTIs following cystoscopy. They were admitted to the urology department of the hospital after visiting the Emergency Department. P. aeruginosa was found in the urine cultures of 4 of the 6 hospitalized patients. During the epidemiological investigation, no changes were observed in factors such as the reprocessing procedures for endoscopic equipment. Therefore, microbiological tests were performed using environmental samples derived from the endoscopic equipment and cleaning process.
Results
P. aeruginosa was identified in a dual-enzymatic detergent (EmPower) used during the endoscope cleaning process. After changing the disinfectant and cleaning process, no further bacterial growth was observed in subsequent microbiological tests.
Conclusions
This study highlights the potential of cystoscopes to serve as reservoirs for bacteria due to inadequate cleaning during the disinfection process. To minimize the risk of infections following cystoscopy, it is important to pay close attention to the reprocessing and cleaning of cystoscopes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Commentary on “Outbreak of Cystoscopy-Related Urinary Tract Infections With Pseudomonas aeruginosa in South Korea, 2022: A Case Series”
Byoungkyu Han
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 52. CrossRef
- A Commentary on “Outbreak of Cystoscopy-Related Urinary Tract Infections With Pseudomonas aeruginosa in South Korea, 2022: A Case Series”
- 3,692 View
- 64 Download
- 1 Crossref

Review Article
- Postoperative Microscopic Pyuria and Role of Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern: A Literature Review
- Min-Kyu Kim, Ki Hong Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(3):73-79. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2448026013
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - All patients who undergo transurethral prostate surgery exhibit pyuria and microscopic hematuria in postoperative urinalysis. Postoperative asymptomatic pyuria is associated with the inflammatory process and surface remodeling of the prostate, rather than infection. Various studies have investigated the incidence, duration, and risk factors for postoperative pyuria, noting that factors like age, surgery time, and prostate size can influence outcomes. Postoperative pyuria reflects tissue recovery and inflammation, and the use of antibiotics in asymptomatic patients may not be appropriate.
- 4,647 View
- 27 Download

Case Report
- Klebsiella pneumoniae-Induced Emphysematous Prostatic Abscess Accompanied by a Spinal Cord Infarction: Case Report
- Seong Uk Jeh, Min Sung Choi, Chang Seok Kang, Dae Hyun Kim, Jae Hwi Choi, See Min Choi, Sung Chul Kam, Jeong Seok Hwa, Jae Seog Hyun
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(3):104-108. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2448024012
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
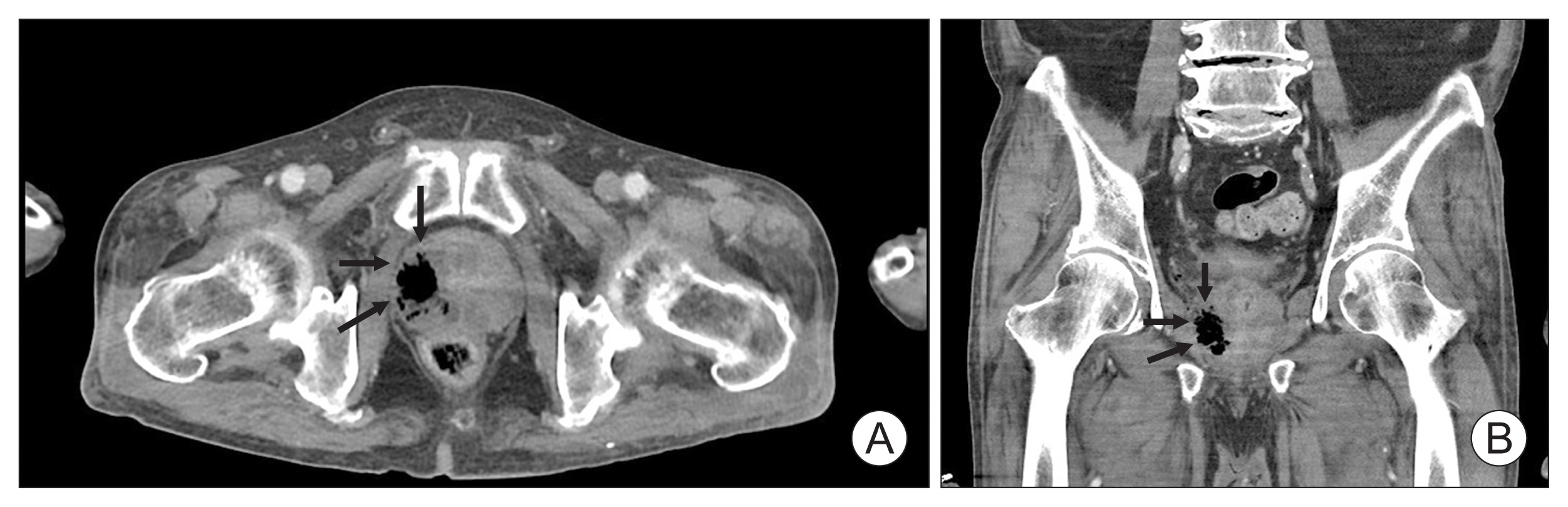
ePub - Various strains can be found in emphysematous prostatic abscesses (EPAs), but the most frequent causative organism is Klebsiella pneumoniae . Hypervirulent K. pneumoniae can disseminate to distant sites by forming a muco-polysaccharide network outside the capsule. Here, we present the first case of K. pneumoniae in an EPA accompanied by a spinal cord infarction. A 65-year-old man was referred to our hospital due to sudden-onset paraplegia after a 5-day history of fever, myalgia, and voiding difficulty. Abdominal computed tomography revealed a collection of air pockets in the prostate, and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging showed high signal intensity in the thoracic spinal cord. The patient was initially treated with antibiotics and surgical drainage. On the third hospital day, therapeutic heparin was added after discussion with a neurologist. The patient had no inflammatory symptoms, experienced some improvement in paraplegia, and was discharged on the 14th hospital day. This study adhered to the case report guidelines.
- 1,968 View
- 23 Download

Review Articles
- Mechanistic Insights Into Persistent Bacterial Cystitis as a Basis for Vaccine Development: A Narrative Review
- Karen Serrano-Arevalo, Manisha Naskar, Hae Woong Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(3):60-72. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2448022011
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
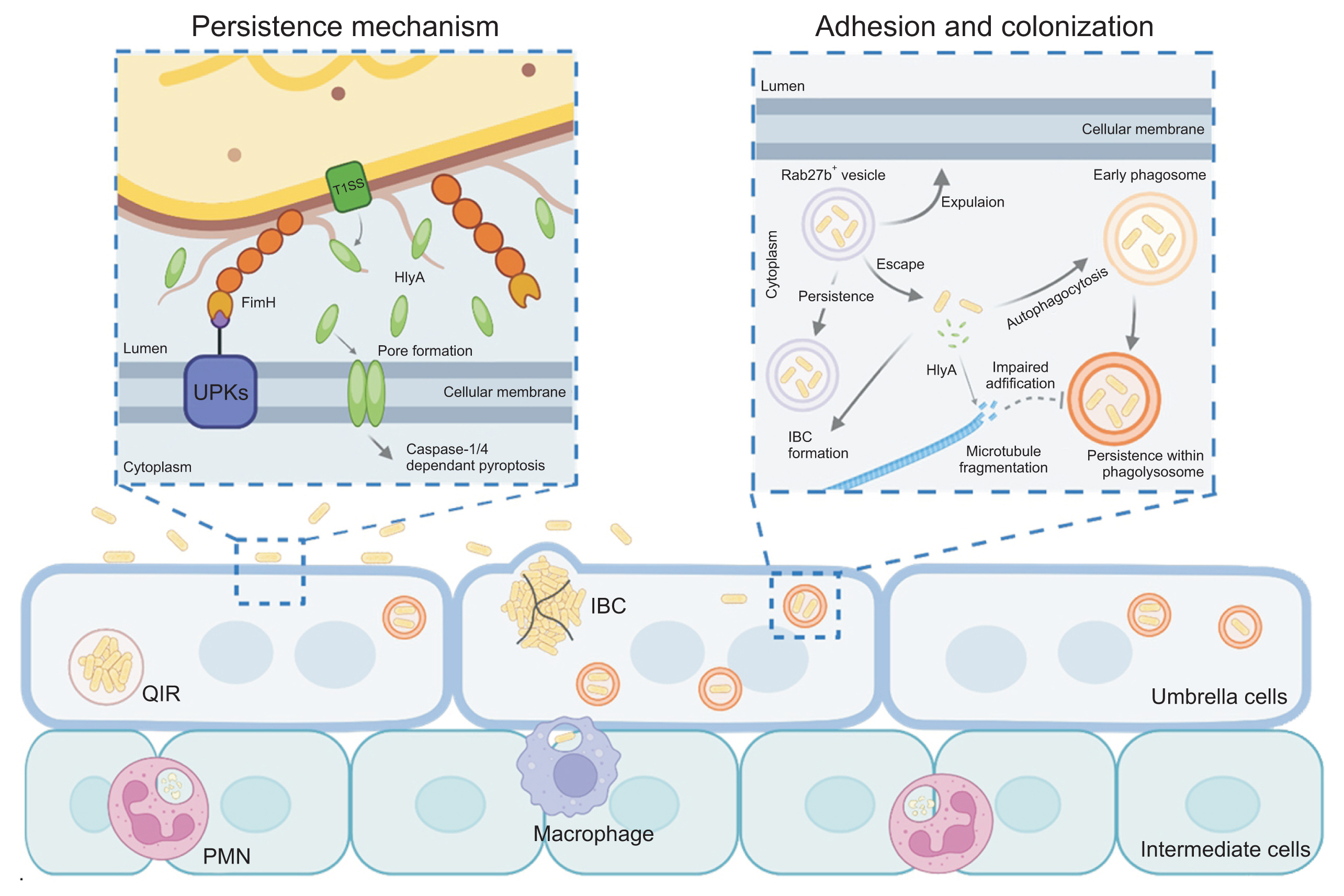
ePub - Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are primarily caused by uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC), which frequently lead to recurrent infections. These bacteria utilize several strategies to establish infection in the host; in particular, virulence factors such as fimbriae and α-hemolysin facilitate persistent infection, evade host immune responses, and minimize antibiotic exposure. To date, antibiotics have been the primary treatment for UTIs. However, an increasing emphasis has been placed on the need for UTI vaccines, with mucosal vaccine products now available in several countries. Additionally, vaccines targeting intracellular UPEC, utilizing adjuvants, are currently under development. Understanding the pathogenic mechanisms of uropathogens has enabled the development of new treatment approaches, paving the way for next-generation preventive and therapeutic methods that could effectively manage recurrent UTIs in the future.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bacterial biofilm – as a contributor to urinary tract infections
Zuzanna Trześniewska-Ofiara, Mariola Mendrycka, Agnieszka Woźniak-Kosek
Biuletyn Głównej Biblioteki Lekarskiej.2025; 58(384): 83. CrossRef
- Bacterial biofilm – as a contributor to urinary tract infections
- 6,328 View
- 56 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Artificial Intelligence for Autonomous Robotic Surgery in Urology: A Narrative Review
- Dae Young Lee, Hee Jo Yang
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(3):80-88. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2448020010
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
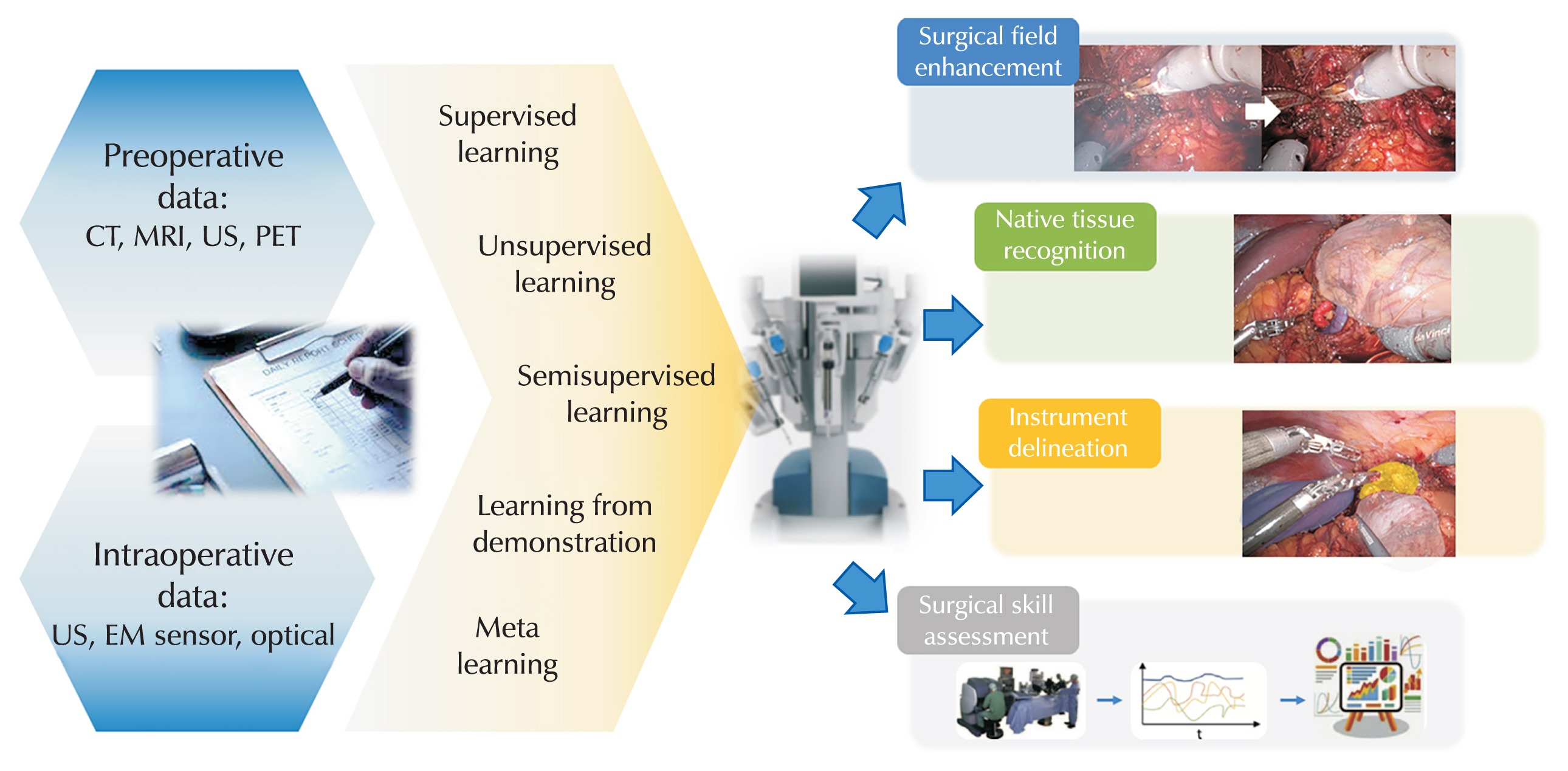
ePub - Artificial intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force in various sectors, including medicine, where it processes high-dimensional data to improve diagnostics and treatment outcomes. This review explores AI applications in urological surgery, highlighting advancements such as image classification and robotic assistance in surgical procedures. AI has demonstrated exceptional diagnostic accuracy, with some systems achieving up to 99.38% in detecting prostate cancer. Additionally, AI facilitates real-time anatomical recognition and instrument delineation, increasing surgical precision. While current robotic systems operate under human supervision, ongoing research aims to advance autonomous surgical capabilities. The future of AI in robotic surgery is promising, especially regarding the possibility of improved outcomes; nonetheless, challenges related to autonomy, safety, and ethics remain.
- 13,098 View
- 162 Download

Original Article
- Impact of the Timing of Percutaneous Nephrostomy on the Prognosis of Obstructive Urolithiasis With Sepsis: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- Ji Eun Yu, Hyung Joon Kim, Hong Wook Kim, Young Seop Chang, Jin Bum Kim, Dong Hoon Koh
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(3):89-96. Published online December 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2448018009
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose
The aim of this study was to investigate the prognostic impact of time to percutaneous nephrostomy (PCN) insertion on obstructive ureteral stones with sepsis. Materials and Methods: Data were collected on patients who presented at our Emergency Department between 2017 and 2021 with obstructive uropathy due to urinary stones and underwent PCN insertion. Patients were stratified into 4 groups in accordance with the quick sepsis-related organ failure (qSOFA) score at presentation (<2 or ≥2) and time to PCN insertion (<4 hours or ≥4 hours) as follows: group 1, qSOFA < 2 and time to PCN insertion < 4 hours; group 2, qSOFA < 2 and time to PCN insertion ≥ 4 hours; group 3, qSOFA ≥ 2 and time to PCN insertion < 4 hours; group 4, qSOFA ≥ 2 and time to PCN insertion ≥ 4 hours. The prognostic impacts of the time to PCN insertion were compared between these groups
Results
The total cohort consisted of 96 patients, of whom 70 were classified as either group 1 or 2 (qSOFA < 2). Overall, 37 patients had a positive urine culture. The median time to PCN insertion was 218 minutes, and the median length of stay was 14 days. The hospitalization period was significantly shorter in group 3 than in group 4 (p=0.041).
Conclusions
A shorter length of stay was associated with more rapid PCN insertion in patients with obstructive uropathy and a high risk of sepsis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Characteristics, Microbiological Spectrum, Biomarkers, and Imaging Insights in Acute Pyelonephritis and Its Complicated Forms—A Systematic Review
Marius-Costin Chițu, Teodor Salmen, Paula-Roxana Răducanu, Carmen-Marina Pălimariu, Bianca-Margareta Salmen, Anca Pantea Stoian, Viorel Jinga, Dan Liviu Dorel Mischianu
Medicina.2026; 62(1): 222. CrossRef
- Clinical Characteristics, Microbiological Spectrum, Biomarkers, and Imaging Insights in Acute Pyelonephritis and Its Complicated Forms—A Systematic Review
- 4,313 View
- 38 Download
- 1 Crossref

Case Reports
- Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy for the Treatment of Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome: Case Report
- Kwang Jin Kim, Yoonsuk Lee, Yong Sung Cha, Tae Wook Kang, Hyun Chul Chung, Hong Chung, Hyun Kim, Jae Hung Jung
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(2):44-47. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.2.44
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) was conducted on two male patients with chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome who were resistant to conventional medical therapies. Both patients underwent 20 sessions of 100% oxygen inhalation (2.0 atmosphere absolute for 90 min/day, five days/week for four weeks) in a hyperbaric chamber. The follow-up period was three months. Although the patients reported a slight improvement in the pain domain of the National Institutes of Health-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) after HBOT, no changes were noted in the other domains of NIH-CPSI and International Prostate Symptom Score. No adverse events were encountered during or after HBOT.
- 4,909 View
- 35 Download

- Robotic Excision of a Huge Seminal Vesicle Cyst, Including Intracystic Papillary Adenoma, Saving Fertility
- Tae Hoon Oh, Ill Young Seo
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(2):40-43. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.2.40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
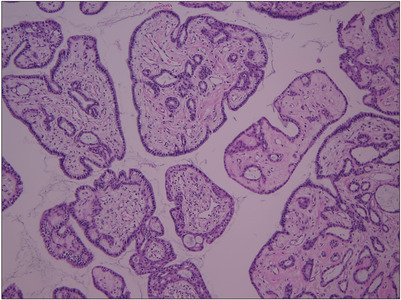
ePub - A seminal vesicle cyst is a rare disease, and an intracystic papillary adenoma within the seminal vesicle is extremely rare. The diagnosis and treatment of these diseases are challenging because of the limited data. This paper presents a robotic excision of a huge seminal vesicle cyst, including an intracystic papillary adenoma, preserving fertility in a 40-year-old man.
- 2,577 View
- 14 Download

Original Articles
- Effect of Residual Stone Fragments on Patient-Reported Quality of Life after Endoscopic Kidney Stone Surgery
- Sang Hee Lee, Jun-Koo Kang, Jae-Wook Chung, Yun-Sok Ha, Jun Nyung Lee, Seock Hwan Choi, Hyun Tae Kim, Tae-Hwan Kim, Eun Sang Yoo, Tae Gyun Kwon, Bum Soo Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(2):31-39. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.2.31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
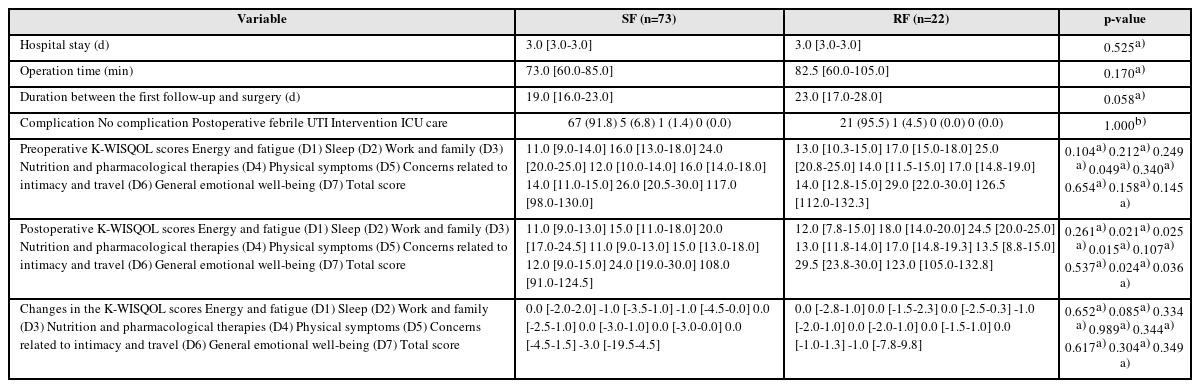
ePub - Purpose: This study examined the effects of residual fragments (RF) on the patient-reported quality of life (QOL) after kidney stone surgery, such as retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) and percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL), using the Korean version of the Wisconsin Stone Quality of Life Questionnaire (K-WISQOL).
Materials and Methods: The medical records of 156 patients who underwent RIRS or PCNL and completed the preoperative and postoperative K-WISQOL from January 2021 to September 2023 were analyzed retrospectively. The patients were divided into RIRS and PCNL groups by the surgical method. The participants completed the K-WISQOL within four weeks before and after treatment. The patients’ baseline characteristics, surgical outcomes, and K-WISQOL scores were compared according to the presence of RF in each surgical group.
Results: Of the 156 patients, 95 underwent RIRS, and 61 underwent PCNL. In the RIRS group, the patients’ baseline characteristics and surgical outcomes were similar in the stone-free (SF) and RF subgroups. The changes in all K-WISQOL domain scores and total scores were similar in the two subgroups. In the PCNL group, the RF subgroup had a significantly higher proportion of staghorn stones, a significantly larger mean stone diameter and significantly longer operation time than those of the SF subgroup. But, the changes in all K-WISQOL domain scores and total scores were not significantly different between the two subgroups, as observed in the RIRS group.
Conclusions: This study showed that the presence of RFs after endoscopic kidney surgery did not affect the short-term patient-reported QOL regardless of the surgical methods.
- 3,289 View
- 39 Download

- Trend Analysis of Sexually Transmitted Infection Treatments in Korea
- Soeon Park, Byung Kyu Han, Sangrak Bae, Seung-Ju Lee, Jin Bong Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(2):25-30. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.2.25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
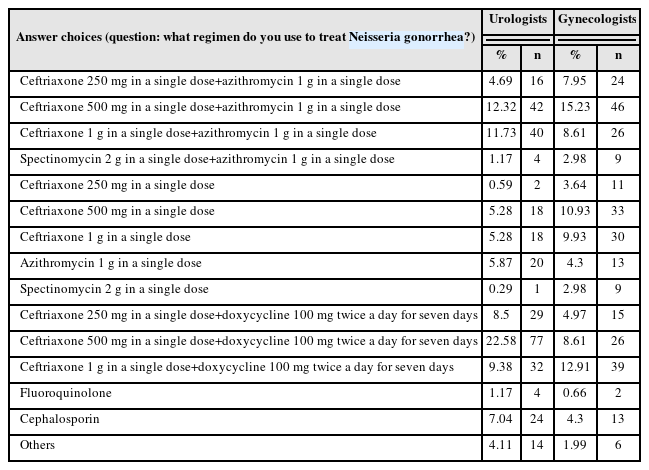
ePub - Purpose: The revision of the 2023 Guidelines for the Treatment of Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) has been released. Hence, it is necessary to analyze the current status of STI treatments in Korea.
Materials and Methods: A questionnaire was distributed to urologists and gynecologists from December 2022 to January 2023 through an online survey program. Three hundred and forty-one urologists and 302 gynecologists responded to the questionnaire.
Results: For Neisseria gonorrhea treatment, ceftriaxone 500 mg and 100 mg of doxycycline twice daily for seven days were most preferred by urologists (22.58%). The treatment most preferred by gynecologists (15.23%) was 500 mg of ceftriaxone and 1 g of azithromycin in a single dose. Both urologists and gynecologists generally treat Chlamydia trachomatis according to the treatment guidelines. For treating Mycoplasma genitalium, 29.03% of urologists preferred administering azithro-mycin at 500 mg once daily, followed by 250 mg for four days. In contrast, 33.11% of gynecologists preferred doxycycline 100 mg twice daily for seven days.
Conclusions: Most urologists and gynecologists followed the treatments recommended in the 2nd edition of the STI treatment guidelines, revised in 2016. As many treatment regimens have changed because of the recent increase in antibiotic-resistant STIs, there is a need to encourage them to follow the new treatment guidelines. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Study of the Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Sexually Transmitted Infections Diagnosed by Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests
Jung Soo Son, Namhee Kim, Hong Sang Oh, Sang Won Park, Dong Hoon Shin
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparative Study of the Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Sexually Transmitted Infections Diagnosed by Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests
- 6,464 View
- 36 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Does Music Have a Calming Effect on Pain and Anxiety in Patients Undergoing Cystoscopy?
- Ye Chan Joo, Ji Eun Yu, Jae Hyun Baik, Young Seop Chang, Jin Bum Kim, Hyung Joon Kim, Dong Hoon Koh, Hong Wook Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(1):3-9. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.1.3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
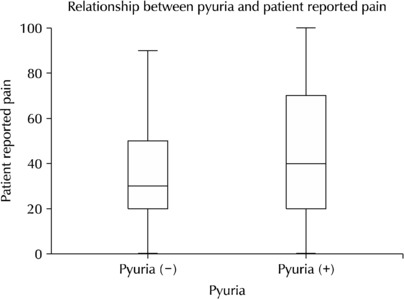
ePub - Purpose: Cystoscopy is a diagnostic test performed frequently in urology outpatient clinics. Despite the large number of inspections, the associated pain, discomfort, or anxiety can markedly affect patient compliance and adherence to subsequent surveillance protocols. This study conducted a prospective, randomized study to investigate the potential efficacy of music and pyuria on pain or anxiety during outpatient cystoscopy.
Materials and Methods: In this single-institution, randomized study, the participants were assigned to a music-intervention or non-music control group. The music-intervention group underwent an identical procedure with the addition of Johann Sebastian Bach’s “Air on the G String” from Suite No. 3 in D major, BWV 1068. Urinalysis was performed to determine if pyuria affects pain during the procedure.
Results: The patient-reported outcomes, encompassing the changes in the STAI-X-1 (State-Trait Anxiety Inventory-X-1) scores, subjective levels of discomfort, embarrassment, satisfaction, and pain, were similar in the two groups. In contrast, the surgeons reported statistically significant differences in their evaluations of the same items as patient-reported outcomes of the two groups. The patient-reported pain showed no significant differences between the pyuria-negative group (0-2 and 3-5 WBC/HPF) and pyuria-positive group (>5 WBC/HPF).
Conclusions: The data from this study do not support the hypothesis that musical intervention during cystoscopy alleviates pain or anxiety to any significant extent. In addition, pyuria did not affect the patient’s reported pain. Nevertheless, a notable impact was observed in the surgeons’ assessments, suggesting that the musical accompaniment may alter the surgeons’ perception of patient pain and anxiety levels throughout the procedure.
- 2,679 View
- 34 Download

- Pelvic Pain in Men with Mycoplasma Genitalium
- Yumi Seo
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(1):16-23. Published online April 30, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.1.16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
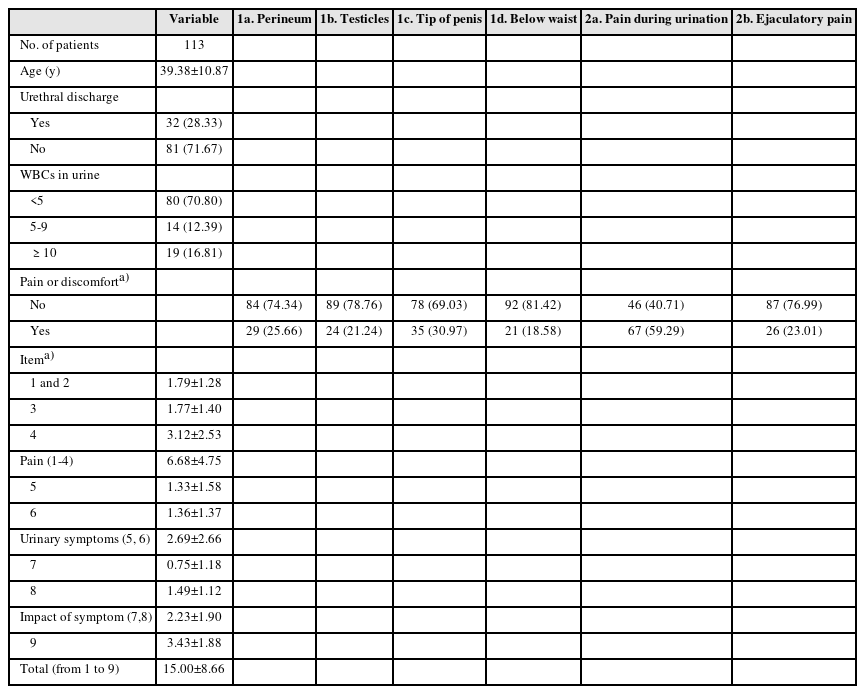
ePub - Purpose: There are debates about Mycoplasma genitalium (M. genitalium) causing prostate infection and inducing pelvic pains. Consequently, M. genitalium-associated pelvic pains were characterized and their manifestation in male pelvic pain syndrome (MPPS) was evaluated through a case-control study.
Materials and Methods: The presence of M. genitalium-associated pelvic pains was examined in 113 M. genitalium-infected men, and the typical presentations of mycoplasma-associated MPPS were characterized through a case-control study involving 80 mycoplasma-infected and 234 case-matched uninfected controls. Finally, changes in symptoms following antimicrobial treatments were compared between 27 cured and 14 persistently infected cases.
Results: Pain locations from 113 men were followed as items-1a for 25.7%, 1b for 21.2%, 1c for 31%, 1d for 18.6%, 2a for 59.3%, and 2b for 23% from the Korean National Institutes of Health-Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI) questionnaire. In addition, the sum scores from the pain domain, voiding domain and total score were 6.68±4.75, 2.69±2.66, and 15.00±8.66, respectively. Successful antibiotic therapy significantly reduced the total score from baseline (15.148±6.798 vs. 5.357±7.025, p=0.001). From the case-control study, mycoplasma-infected men had pains more frequently during urination (1c) and on the tip of the penis (2a) (all p=0.0001) than the controls.
Conclusions: It was found that M. genitalium infection is associated with clinically significant male pelvic pains, which improved with adequate antimicrobial therapies. Urethral irritation symptoms without pyuria may be the typical characteristics of mycoplasma-associated pelvic pains in MPPS.
- 6,727 View
- 29 Download


 KAUTII
KAUTII

 First
First Prev
Prev