Abstract
Kidney disease poses a major and growing global health challenge, with both prevalence and mortality continuing to rise. Current standard-of-care treatments, including dialysis and kidney transplantation, have significant limitations and do not adequately meet clinical needs. This unmet need has driven the development of next-generation regenerative medicine strategies, which can be broadly categorized into 3 areas: (1) approaches that enhance the kidney’s limited intrinsic regenerative capacity; (2) stem cell-based therapies; and (3) implantable bioengineered kidney constructs. This review summarizes recent advances in each of these domains and discusses the major biological, technical, and regulatory challenges that must be addressed to enable successful clinical translation.
-
Keywords: Kidney, Regeneration, Cell- and tissue-based therapy, Bioengineering, Regenerative medicine
HIGHLIGHTS
Current standards of care for kidney dysfunction are limited to symptom management and slowing disease progression. To address this unmet clinical need, new regenerative medicine strategies are emerging, including the use of stem cells, enhancing intrinsic regenerative capacity, and employing bioengineered kidney constructs. Future work will focus on overcoming biological, technical, and regulatory challenges to enable the safe and effective clinical integration of these novel therapies.
INTRODUCTION
The kidneys are highly complex organs responsible for a range of critical physiological functions, including fluid and electrolyte balance, ultrafiltration of waste products, metabolism, hormone production, and the reabsorption and secretion of various substances. Their continuous operation is essential for maintaining systemic homeostasis.
Kidney dysfunction—including acute kidney injury (AKI), chronic kidney disease (CKD), and end-stage renal disease (ESRD)—poses a substantial healthcare challenge with increasing prevalence worldwide. AKI affects 114–174 individuals per 10,000 person-years, with mortality rates reported at 24% in adults and 14% in children [
1]. CKD is currently the ninth leading cause of death worldwide, affecting over 9% of the global population, including 25% of adults over the age of 60, and accounting for an estimated $270 billion annually in direct healthcare costs [
2-
5].
Renal failure typically unfolds through a series of stages of increasing severity. It often begins with AKI, a sudden decline in renal function triggered by various factors, such as environmental stress (e.g., heat and dehydration), inflammation, infections, major surgery, cardiovascular or hepatic conditions, pregnancy complications, and exposure to toxins. Without timely and effective intervention, AKI can progress to CKD, and eventually to ESRD, where the kidneys can no longer sustain life-supporting functions due to significant irreversible damage and progressive irreversible fibrosis of the renal parenchyma. As kidney disease progresses and increases in severity, it can lead to dysfunction in other organs (e.g., heart, liver, brain, immune system), causing multi-organ failure in severe cases [
1,
6]. Moreover, patients with advanced renal diseases are at an increased risk of kidney cancer [
7].
CURRENT TREATMENT APPROACHES AND THEIR LIMITATIONS
Current standards of care for kidney dysfunction primarily focus on managing symptoms and slowing down the disease progression, rather than on addressing or reversing the underlying pathology. These therapies mainly aim to correct fluid and electrolyte imbalances, with limited impact on other essential renal functions or the causes of the kidney failure [
8].
At the early stages, the kidney disease progression can be attenuated through lifestyle modifications, pharmacological therapies, and surgical interventions [
5]. The lifestyle changes typically involve sodium and protein dietary restrictions. Pharmacological therapies are directed at reducing hypertension, glomerular hyperfiltration, inflammation, fibrosis, and proteinuria. Bariatric surgery has also shown efficacy in improving renal outcomes in obese patients [
5]. However, as the disease progresses, these interventions become increasingly ineffective [
9], leaving hemodialysis and donor kidney transplantation as the primary treatment options.
Hemodialysis—mechanical removal of metabolic waste and excess fluid through ultrafiltration—has been the standard-of-care treatment for patients with severe kidney disease. It remains the most widely used option due to the limited availability of donor organs. However, hemodialysis presents serious limitations. It is associated with reduced quality of life and patients’ autonomy, as treatments are required multiple times a week in clinical settings. The requirement for complex equipment and specialized personnel results in high healthcare costs [
8,
9]. From a technical standpoint, dialysis is limited in its ability to effectively clear middle- and large-molecule solutes and poses a risk of infection and cardiovascular diseases [
10,
11]. Physiologically, dialysis fails to replicate several critical kidney functions, such as selective reabsorption, immune regulation, metabolic roles (e.g., vitamin D and glutathione metabolism), and endocrine activities (e.g., renin and erythropoietin production) [
6,
11,
12].
Recent advances in dialysis have focused on addressing the above shortcomings. Innovations in new membrane materials have improved blood purification characteristics and fluid control [
10,
11]. A new generation of dialysis devices—bioartificial kidneys—aims to integrate semipermeable dialysis membranes with biological components (renal cells) to better emulate native nephron functions [
10,
11]. While these devices offer a more physiologically relevant solution than traditional dialysis, they still face significant technical and regulatory hurdles, including maintaining long-term cell viability, preventing clotting, and ensuring uniform blood flow. Therefore, dialysis still remains a life-sustaining, but not curative therapeutic option [
8,
11].
Kidney transplantation—the surgical replacement of the dysfunctional kidney with a healthy organ from a living or deceased donor—is currently the most effective treatment option for restoring full renal function. It provides significant improvements in patient survival and quality of life [
10,
13]. However, it is limited by a shortage of donor organs, the need for lifelong immunosuppression, risk of graft failure, and potential recurrence of the native disease [
6,
8,
13,
14]. Moreover, despite advances in techniques and post-operative care, patient survival remains an issue. Transplant recipients still face an up to 10-fold higher mortality risk compared to the general population [
15].
In the following sections, we review the development of next-generation therapeutic approaches directed at the curative treatment of kidney dysfunction through regenerative medicine strategies. To provide appropriate context, we preface this discussion with an overview of kidney organization, highlighting its structural and functional complexity. We also briefly summarize the intrinsic regenerative response to kidney injury, which often becomes maladaptive, thereby contributing to disease progression rather than leading to recovery.
OVERVIEW OF KIDNEY ORGANIZATION
Despite constituting only 0.5%–1% of the total human body weight, the kidneys receive 20%–25% of the resting cardiac output. This disproportionately high blood flow is necessary for the kidneys to efficiently perform their filtering functions and maintain systemic homeostasis [
16,
17]. The mature adult human kidney exhibits a complex microanatomical and histological organization, which is critical for its function. It is made up of at least 16 highly specialized renal cell types, which are organized into structurally and functionally distinct units—nephrons. Below, we highlight several of these cell types along with their key features and functions.
Each nephron consists of a glomerulus and a long slender renal tubule, which is further subdivided into proximal, intermediate, and distal segments. To support renal function, the circulatory system must form a complex anatomical arrangement with the epithelial structures of the nephron. Each nephron is supplied with 2 sequential capillary systems formed by specialized endothelial cells. Glomerular capillaries receive the blood from afferent arterioles and carry out the primary filtration into the surrounding Bowman’s capsule. The glomerular capillaries then converge into efferent arterioles, which subsequently branch again to give rise to peritubular capillaries, which are responsible for the reabsorption of water and solutes back into the blood plasma [
17].
Mesangial cells within the glomerulus perform several key maintenance functions. They provide structural support, produce components of the glomerular extracellular matrix (ECM), regulate capillary blood flow, remove cellular debris by phagocytosis, and secrete growth factors that support the glomerulus [
17].
Podocytes are epithelial cells that form the inner (visceral) wall of the Bowman’s capsule and wrap around the basal lamina of the glomerular capillaries. Together with the endothelial cells and the endothelial basal lamina, podocytes form the filtration barrier in the glomerulus and thus contribute to selective filtration. Podocytes also secrete vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A), a growth factor critical for the survival and function of glomerular endothelial cells [
17].
Renal tubules are composed of several different cell types, which occupy distinct locations along the length of the tubule and serve specific functions. Proximal tubular cells are the most abundant cell type in the kidney and are responsible for the reabsorption of water, electrolytes, and nutrients (e.g., glucose, amino acids, etc.) from the primary filtrate [
17].
In addition to the epithelial and mesangial cells of the nephron, the healthy kidney contains a diverse population of immune cells, including macrophages, neutrophils, lymphocytes, and natural killers, indicating constitutively occurring immune surveillance [
17]. The renal interstitium—the extravascular/intertubular spaces of the renal parenchyma—contains fibroblasts, myofibroblasts, as well as erythropoietin- and renin-producing cells.
PHYSIOLOGICAL CELL TURNOVER IN THE KIDNEY
Normal functions in the kidney are largely carried out by postmitotic cells with minimal turnover. In most renal cell types, the cell cycle is arrested in the G0 phase, reflecting a highly quiescent state [
18]. For example, adult podocytes are fully differentiated and incapable of mitotic division [
18,
19]. Renal tubule cells in an unstressed normal kidney divide at a slow rate, adding on average one new tubular epithelial cell per nephron per day. This slow cell turnover is sufficient to offset physiological cell loss and maintain epithelial integrity [
18]. Mesangial cells are also mostly quiescent in the normal adult kidney, with little evidence of turnover under baseline conditions [
18].
PATHOLOGIES OF KIDNEY DYSFUNCTION AND MALADAPTIVE COMPENSATORY RESPONSE
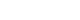
Early phases of AKI are characterized by neutrophil recruitment. Neutrophils, in turn, recruit macrophages. The consequences of the macrophage recruitment are twofold. First, they facilitate wound healing and subsequent tissue repair. However, their long-term presence can also contribute to exacerbating the tissue damage and lead to a failure of tubular repair and kidney fibrosis (
Fig. 1) [
1].
Kidney injury triggers the DNA damage response pathway, which induces cell cycle arrest and, eventually, cell senescence or death in tubular and glomerular cells, thereby impairing regenerative capacity (
Fig. 1). Senescent and necrotizing cells secrete potent proinflammatory and profibrotic mediators, which interfere with tissue repair, further damage the neighboring healthy cells, suppress cell proliferation and migration, as well as stimulate collagenous ECM deposition, leading to tubular atrophy and glomerulosclerosis. The number of podocytes covering the glomerular capillaries decreases, leading to the impaired filtration function and the glomerular leak of plasma proteins [
7,
15,
16,
18,
20].
Tubular epithelial cells are highly sensitive to disruptions in metabolic homeostasis within the kidney. Due to their energy-demanding functions of active transport, these cells are required to maintain a high mitochondrial density. Kidney injury results in mitochondrial fragmentation and dysregulation in these cells, leading to the depolarization and increased permeabilization of the mitochondrial membrane and subsequent release of intracellular proapoptotic factors (
Fig. 1). If the cells do not undergo rapid apoptosis, they experience adenosine triphosphate (ATP) depletion and elevated production of reactive oxygen species caused by the mitochondrial impairment. This energy deficit leads to the disruption of the normal cytoskeletal architecture, loss of the apical brush border, breakdown of intercellular junctions, and cell detachment [
21].
In embryogenesis, the complex kidney microanatomy and tissue organization emerge through highly coordinated reciprocal interactions between the metanephric mesenchyme and the ureteric bud. Both structures contain stem cell populations that generate distinct differentiated cell types that eventually form the mature kidney. It is conceivable that these developmental events could be re-enacted to support kidney regeneration after injury. However, such nephrogenic events are restricted to the embryonic period, as the metanephric mesenchyme progenitor cells that give rise to the proximal nephron, including podocytes, during kidney development, disappear from the mammalian kidney shortly after birth [
19].
The adult kidney's largely postmitotic and terminally differentiated cell population lacks intrinsic capacity for efficient post-traumatic nephrogenesis. While kidney injury induces extensive necrosis and apoptosis followed by a transient proliferative burst in tubule cells and macrophages [
22], resulting in partial regeneration of necrotic renal tubules (replacing ≤50% of injured cells) [
23,
24], lost nephrons are not functionally replaced as structural units [
18,
25]. To a degree, this loss is compensated by hypertrophy and functional hyperactivation of the surviving nephrons. While initially beneficial, this compensation ultimately exacerbates the renal damage by imposing long-term stress and damage in the remaining nephrons [
7,
16]. For example, hyperfiltration (the increase in the hydrostatic pressure) damages podocyte foot processes and cell bodies (
Fig. 1) [
7].
At the level of individual cell types, podocytes may attempt to re-enter the cell cycle and replicate their DNA, but ultimately cannot complete cytokinesis and either undergo mitotic catastrophe followed by cell death or become polyploid, thus failing in either case to restore the podocyte number lost to injury [
7,
18].
AKI triggers profound changes in renal tubular epithelial cells. These cells secrete profibrotic and proinflammatory factors (e.g., interleukin [IL] 11, IL33, CCL20, and CXCL8), lose their brush border, and undergo cell death via apoptosis and regulated necrosis [
4,
7]. Surviving tubular cells can dedifferentiate and undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a process regulated by the repression of the cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin by the transcriptional repressor SNAI1 [
4]. This EMT yields collagen-producing cells, which ultimately contribute to interstitial fibrosis and chronic kidney damage (
Fig. 1) [
26].
Upon injury, mesangial cells can be replaced by the proliferation of local progenitors. However, persistent production of mesangial cells, coupled with ECM production, can lead to progressive glomerular damage [
18].
In summary, kidney injury initiates a cascade of cellular and molecular events that, although initially aimed at repair, ultimately shift toward maladaptive responses. The limited intrinsic regenerative capacity of the adult kidney, combined with ongoing inflammatory and fibrotic processes, leads to progressive structural deterioration and functional decline. A deeper understanding of these mechanisms is essential for developing effective regenerative therapies that can restore both the structure and function of the kidney.
REGENERATIVE MEDICINE STRATEGIES
The human kidney has limited intrinsic regenerative capacity, and current standard treatments have notable limitations. These challenges have led to significant efforts in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine to develop new therapeutic approaches, such as bioengineered kidney implants and cell-based therapies. These emerging approaches generally fall into one or a combination of the following 3 categories:
• Facilitation of intrinsic regeneration
• Stem cell therapies
• Organ replacement with tissue-engineered analog
1. Boosting Endogenous Kidney Regeneration
As discussed above, the kidney responds to injury by initiating a tissue repair response. However, this endogenous repair process is often disrupted and stalled due to several factors, including the postmitotic state of many renal cell types, the kidney’s inherent structural and functional complexity, and the need to maintain homeostatic functions during regeneration. Paradoxically, this dysregulated repair can even contribute to further progression of kidney pathology rather than resolving it.
One of the major therapeutic goals in enhancing endogenous kidney regeneration is to inhibit profibrotic EMT in proximal tubular epithelial cells (see above), while promoting their re-entry into a proliferative and reparative state. EMT, a key contributor to fibrosis, is triggered by autocrine IL11 signaling in response to injury.
In preclinical animal models, targeting IL11 has been shown to prevent, reduce, and even reverse tubular EMT, inflammation, tissue damage, and fibrosis. Importantly, IL11 inhibition also enhances intrinsic repair mechanisms by promoting tubular cell proliferation, restoring parenchymal tissue mass, and improving renal function [
26]. These findings suggest that IL11 inhibition may unlock the kidney’s innate regenerative capacity and represents a promising therapeutic approach for both acute and CKDs. Based on these promising results, a phase I clinical trial [
27] was launched in 2022 to evaluate the safety profile and preliminary efficacy of anti-IL11 antibody therapy in human patients.
Another class of agents shown to support intrinsic kidney regeneration is histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDAC). Compounds such as trichostatin and 4-phenylbutyrate have been shown to promote tubular regeneration by stimulating the proliferation of Pax2
+ tubular progenitor cells (see below) [
23]. HDAC inhibitors also reduced renal interstitial fibrosis—a major hallmark of CKD—by suppressing the profibrotic transforming growth factor-beta and upregulating the expression of the antifibrotic protein BMP7 [
27].
Efforts to develop stem cell-based therapies to treat kidney diseases have primarily focused on 2 main strategies: supplementing kidney-specific stem/progenitor cells and administering mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs). The former approach aims to directly replenish damaged or lost renal cells by delivering progenitor cells capable of engrafting into injured kidney tissue and differentiating into functional cell types. In contrast, MSC-based therapies are not intended as a direct source of cell replacement. Instead, they aim to accelerate intrinsic kidney regeneration via the paracrine secretion of bioactive factors by infused stromal cells.
1) Kidney progenitor cells
In theory, kidney tissue repair could be supported through therapies employing autologous renal progenitor cells. This approach involves isolating stem/progenitor cell population(s) from the patient, expanding them ex vivo, and then reintroducing them into the diseased kidney. The administered cells would ideally respond to the signaling milieu in the damaged kidney and generate differentiated progeny, contributing to functional repair.
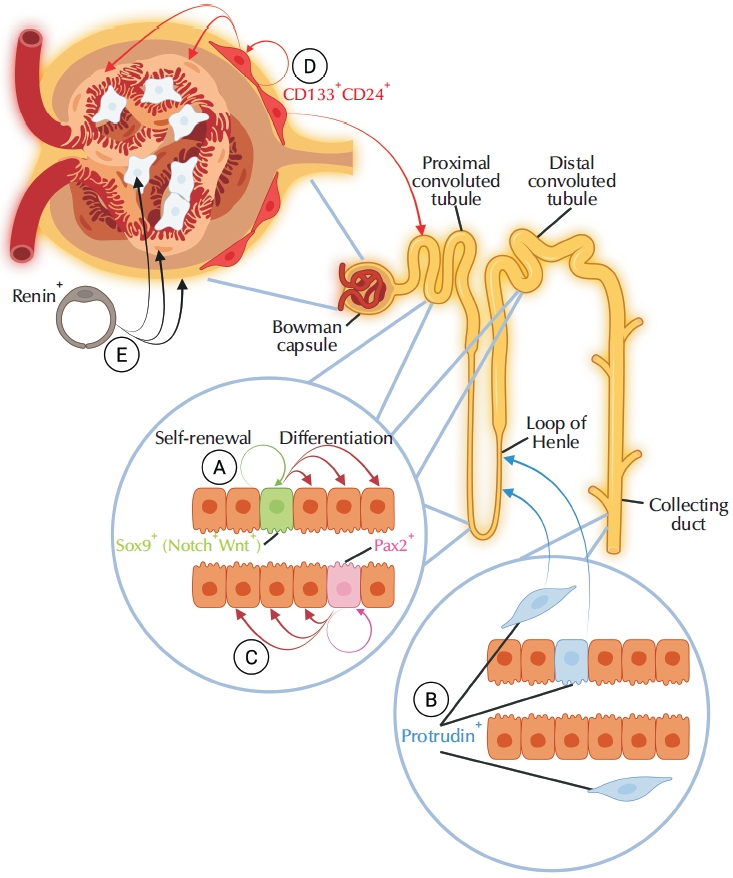
Despite its conceptual promise, this strategy faces several biological and technical hurdles. A major challenge lies in identifying definitive kidney stem/progenitor cells. To date, no multipotent, pan-renal stem cell population capable of differentiating into all major kidney cell types has been identified. Instead, evidence suggests the existence of multiple, fate-restricted progenitor populations (
Fig. 2).
In vivo lineage tracing in animal models suggests that each of those cell populations gives rise to a limited range of differentiated kidney cell types restricted to specific microanatomical locations within the kidney [
28-
30].
2) Renal tubule progenitors
Among the renal progenitor populations, Sox9
+ cells are relatively well characterized (
Fig. 2A). These cells have been shown to contribute to the maintenance and regeneration of the renal tubular epithelium in the proximal tubule, loop of Henle, and distal segments. However, Sox9+ cells do not appear to contribute to glomerular or collecting duct repair. Following injury, the Sox9
+ cell population expands, primarily through the recruitment of surviving proximal tubule epithelial cells. These recruited cells markedly upregulate Sox9 expression, undergo extensive proliferation and clonal expansion, and subsequently differentiate back into mature tubular epithelial cells. In addition to directly generating new epithelial cells, Sox9
+ cells also play an important role in juxtacrine and paracrine signaling, actively expressing Notch and Wnt ligands, which are key regulators of kidney development and repair. Notably, a transient spike in Notch signaling has been associated with accelerated regeneration in animal models of kidney injury [
28-
30].
Another progenitor cell population has been identified in the upper part of the renal papilla. These cells express protrudin (Zfyve27) and are mainly localized within the interstitial spaces and in the epithelium of the collecting ducts (
Fig. 2B). Protrudin is involved in interorganellar communication. Although its specific function in stem or progenitor cells remains unclear, it may contribute to cell motility and migration [
24]. Under normal (homeostatic) conditions, the protrudin
+ progenitors cycle very slowly and thus do not significantly contribute to kidney cell turnover. However, after severe kidney injury, these cells become activated and exhibit a distinct regenerative response. They migrate toward the medulla, divide, and produce daughter cells that form long tubular segments that are primarily localized in the medulla [
31].
The third regenerative cell population contributing to renal tubule repair comprises a small subset (≤10% of the total cell population) of tubular epithelial cells expressing Pax2 (
Fig. 2C). These cells are highly resistant to injury-induced cell death and exhibit strong clonogenic potential, distinguishing them from the bulk of the tubular epithelium. In fact, only Pax2+ cells were shown to complete full mitotic division in response to kidney injury. In contrast, other tubule epithelial cells, although capable of DNA replication, became polyploid instead. Despite their regenerative potential, the progeny of Pax2+ cells remain confined to specific tubular segments [
23,
30]. Interestingly, the proliferative activity of Pax2+ progenitors can be enhanced pharmacologically. Treatment with HDAC inhibitors not only promotes their expansion but also reduces tissue fibrosis, suggesting therapeutic potential for enhancing kidney regeneration following injury [
23].
3) Glomerular progenitors
One of the major challenges in effective kidney regeneration is the replacement of podocytes. Adult podocytes cannot self-renew in adulthood as they have irreversibly exited the mitotic cycle. Thus, restoring podocyte numbers must depend on nonpodocyte sources. In fact, it has been established that glomerular podocytes can be regenerated by 2 progenitor cell populations: parietal epithelial cells of the Bowman’s capsule and renin-expressing cells (
Fig. 2D and
E). Genetic lineage tracing suggests that up to 38% of lost podocytes can be replenished after kidney injury [
19].
The parietal epithelial progenitors, located at the urinary pole of Bowman’s capsule, are characterized by the co-expression of 2 stem cell surface markers—CD133 and CD24 (
Fig. 2D). These CD133+CD24+ cells account for 1%–4% of total renal cells and are capable of self-renewal and bipotent
in vitro differentiation into podocytes and tubular epithelial cells under optimized culture conditions [
32]. Although these cells play little to no role in normal renal maintenance, intravenous injection into AKI animal models demonstrated their ability to engraft into glomeruli and tubules. Upon the engraftment, they differentiate into podocytes and proximal tubular cells, reduce glomerular and tubulointerstitial injury and fibrosis, and improve kidney function [
32]. The capacity of parietal epithelial cells to give rise to adult podocytes is consistent with their shared embryonic origin, as both cell types are derived from a common restricted pool of mesenchymal progenitors during embryogenesis [
19,
30].
The CD133+CD24+ progenitors are thus worth considering as a candidate for stem cell-based therapy for renal diseases due to their self-renewal potential,
in vivo engraftment capacities, and differentiation into both glomerular and tubular cell types [
32]. Pharmacological agents, including retinoids, corticosteroids, and GSK3 inhibitors, have been shown to accelerate de novo podocyte generation from these progenitors [
19]. However, a major remaining challenge is to prevent off-target differentiation into irrelevant cell types, such as adipocytes—a phenomenon that can lead to glomerular sclerosis [
32]. Additionally, it remains unclear whether the recruitment of the regenerative progenitors can yield sufficient numbers of podocytes to overcome the critical scarring threshold, which is typically reached at ~20% podocyte loss [
19,
20].
Extraglomerular cells of renin lineage have also been reported to contribute to podocyte regeneration (
Fig. 2E). In addition, they also give rise to intraglomerular mesangial cells and glomerular parietal cells after injury. These renin+ cells are vascular smooth muscle cells that account for ~0.01% of all kidney cells and are confined to the juxtaglomerular compartment under normal conditions. Following acute or chronic podocyte depletion, they migrate from the arteriolar wall into glomeruli and differentiate into podocytes and glomerular parietal cells, while preventing the development of glomerulosclerosis. However, self-renewal of these cells in the adult kidney has not been conclusively demonstrated [
19,
20].
It remains unclear how many distinct progenitor/stem populations exist
in vivo in the kidney. This uncertainty is partly due to the variability in experimental approaches across studies, including the use of different stem cell markers, lineage-tracing techniques, and model systems. The markers that have been used so far to define the progenitor populations might lack strict cell-type specificity, making it difficult to unambiguously differentiate one progenitor pool from another. For example, Sox9+ tubular progenitor cells also coexpress CD133, a marker of glomerular progenitors [
29]. These cells also express Lgr5, which in another study [
33] identified a cell population contributing to the loop of Henle and distal convoluted tubules in kidney development. Likewise, protrudin+ progenitors in the renal papilla express CD133 and CD24, but not Sox9 [
24].
Taken together, these findings suggest that any successful therapy that attempts to harness the naturally occurring regenerative potential in the kidney would likely require a composite clinical cell product comprising multiple ex vivo expanded progenitor cell types. This approach would be necessary to overcome the fate-restricted differentiation potential observed across the individual progenitor populations.
4) Mesenchymal stromal cells
MSCs have emerged as one of the most promising sources for cell-based regenerative therapies in the context of various organs and tissues. Their appeal lies in several advantageous features, including the relative ease of harvesting, capacity for
ex vivo expansion, immunomodulatory and paracrine properties, and multilineage differentiation potential [
34]. While the definition of MSCs still remains somewhat vague, they are generally characterized by (1) adherence to cell culture plastic under standard conditions; (2) the ability to differentiate into at least osteoblasts, chondroblasts, and adipocytes; and (3) the expression of a specific set of surface markers, such as CD105, CD73, and CD90 [
35-
37]. Importantly, unfractionated human MSC preparations are heterogeneous, comprising both true stem cells and other cell types. In this review, we therefore use the term “MSC” to refer to mesenchymal stromal cells, with mesenchymal stem cells considered a subset of this broader category. Nevertheless, somewhat confusingly, in the literature the acronym MSC is often applied interchangeably to refer to either population. Originally discovered in the bone marrow, MSCs have since been identified in and isolated from the perivascular environments of all major organs and tissues.
The therapeutic efficacy of MSCs in kidney disease is largely attributed to 2 key properties: (1) homing to sites of injury after systemic or local administration and (2) their secretion of renoprotective factors once they reach the damaged areas within the kidney [
21,
38]. These bioactive factors include signaling pathway ligands, extracellular vesicles loaded with proteins, mRNAs, or miRNAs, and even intact organelles, such as mitochondria, delivered via intracellular transfer. These factors delay or reverse the kidney disease progression via antiapoptotic, anti-inflammatory, antifibrotic, antioxidative, immunomodulatory, and proangiogenic mechanisms [
6,
7,
12,
14,
38]. In one study, it has been shown that exosomes produced by adipose-derived MSCs induced the upregulation of Sox9 in tubular epithelial cells, thereby activating a native kidney progenitor cell population (see above,
Fig. 2) and promoting tubular regeneration [
38].
Despite their promise, a major challenge associated with MSC-based therapies is the incomplete understanding of their mechanism of action. In particular, the specific cellular targets of MSC-derived paracrine factors and their precise signaling pathways involved are not yet fully defined. This knowledge is critical for the accurate interpretation of the results of the ongoing and future clinical trials involving MSC-based therapies.
One of the examples with a well-characterized mechanism of action involves the use of human umbilical cord-derived MSCs in a mouse AKI model. Following intravenous administration, these MSCs were observed to infiltrate the peritubular areas within the injured renal tissue. Through paracrine signaling, they induced tubular epithelial cells to restore their impaired energy metabolism. In the presence of the MSCs, the tubular cells were able to repair their mitochondrial mass and normalize cell energy metabolism, including antioxidant defenses and ATP production levels. One key mechanism underlying this mitochondrial recovery involved enhanced mitochondrial mobility and intercellular mitochondrial transfer between tubule epithelial cells [
21].
The goal of kidney bioengineering is to increase the availability of transplantable organs, reducing reliance on the very limited pool of human donors. Unlike approaches aimed at promoting in situ regeneration, this approach focuses on the ex vivo preassembly of a fully implantable kidney construct. A key component of this strategy is the development of a supporting scaffold which not only provides structural support but also guides cellular events required for a successful functional maturation of the organ equivalent. Beyond its mechanical role, an ideal scaffold should support and regulate cell attachment, proliferation, migration, survival, differentiation, and intercellular signaling. Crucially, the scaffold should enable the formation of renal cellular units that closely mimic the structure and function of the native kidney.
Scaffolds for the bioengineered kidney are generally derived from one of 2 sources: (1) decellularized ECM obtained from human or animal (e.g., pig, sheep, or goat) kidneys; or (2) manufactured acellular scaffolds produced from biopolymers (e.g., collagen, Matrigel, and hyaluronic acid) or synthetic biodegradable materials (e.g., polyglycolic acid), most often fabricated using 3-dimensional (3D) bioprinting technology [
6].
Among these, native ECM-derived scaffolds tend to outperform artificial alternatives in both mechanical strength and microanatomical fidelity [
6,
14]. Such scaffolds are produced through physical, chemical, or enzymatic decellularization techniques, which aim to remove immunogenic allogeneic or xenogenic cells while preserving the native 3D ECM microarchitecture and macroanatomical structure, as well as functional bioactive substances. Preservation of ECM components—collagens, elastin, glycosaminoglycans, and integrated growth factors—is essential for subsequent cell survival and lineage-specific differentiation. Chemical decellularization commonly employs detergents (e.g., sodium dodecyl sulfate, sodium laureth sulfate, or Triton X-100), enzymes (e.g., DNase, trypsin), bases (e.g., NaOH), and/or chelating agents (e.g., EGTA [ethylene glycol-bis(β-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid]), which together solubilize cellular membranes and remove nuclear and cytoplasmic components. Chemical protocols can be combined with repeated freeze-thaw cycles to speed up decellularization and enhance its efficiency. Cryoprotective compounds may also be applied to minimize the detrimental impact of ice crystals on the ECM microarchitecture.
The ECM composition and growth factors embedded in the scaffold play a critical role in directing the behaviour of seeded cells, including their proliferation, organization, and differentiation. To enhance the scaffold's performance, extrinsic bioactive molecules can be incorporated into the decellularized matrix. For example, VEGF and anti-CD31 antibodies can be added to improve vascularization. Immobilized heparin further prevents thrombosis and reduces inflammation. Treatment with chondroitin sulfate enhances cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation. One of the newest approaches involves the incorporation of MSC-derived extracellular vesicles into scaffolds to further support regeneration [
6,
14,
38,
39].
Prior to implantation, cellular repopulation (recellularization) of the scaffold is essential. Various cell types have been explored in proof-of-concept studies, including embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), MSCs, primary human renal cells, and adult kidney progenitors. Cells are expanded ex vivo and then introduced into the decellularized kidney scaffold, e.g., via perfusion through renal artery, vein, and/or ureter. For example, re-endothelialization of the vasculature is often achieved by injecting endothelial cells through the renal artery and vein.
However, practical and regulatory constraints limit the choice of clinically usable cell types. For example, despite their pluripotency, embryonic stem cells are subject to ethical and legal restrictions. iPSCs, while offering patient-specific advantages, present safety risks including potential immunogenicity and tumorigenicity. Recellularization using autologous patient-specific cells minimizes the risk of immune rejection and improves long-term survival and function. In recent years, substantial effort has been directed toward improving protocols for the isolation and expansion of patient-derived primary renal cells and/or progenitor populations, often obtained from kidney biopsy samples. These advances aim to generate sufficient cell numbers for scaffold seeding and functional tissue reconstruction [
6,
12,
39].
In summary, kidney bioengineering is a dynamic and rapidly advancing field with significant promise. Yet, several key challenges remain before clinical application becomes feasible. For a recellularized kidney to be functional, it must faithfully replicate the native anatomical microarchitecture and cell-type composition of the kidney. Achieving this goal requires continuing effort to optimize scaffold characteristics, refine decellularization protocols, or improve the design and fabrication of bioprinted scaffolds. In addition, further improvements are still needed in kidney cell harvesting, ex vivo expansion, and integration of all relevant cell types into the scaffold during the recellularization process.
TRANSLATIONAL STATUS AND CHALLENGES
1. Ethical and Safety Considerations
The practical range of cell types suitable for clinical applications involving stem/stromal cells or the bioengineered kidney is constrained by several technical limitations. From a purely biological standpoint, pluripotent cells—including embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and iPSCs—hold particular promise due to their ability to differentiate into diverse specialized cell types. However, the use of both these pluripotent cell sources raises serious concerns.
Human ESCs are harvested from the inner cell mass of early blastocyst stage embryos. This process inevitably destroys the embryo—a central issue in ethical debates. Beyond ethics, human ESCs also present practical and safety challenges, including low isolation efficiency and high incidence of chromosomal anomalies resulting in an abnormal karyotype [
40,
41].
iPSCs have emerged as a less ethically controversial alternative to ESCs. They are typically generated from post-embryonic somatic cells by forced overexpression of developmental transcription factors, which reset their differentiated phenotype and restore the pluripotent state. Like ESCs, iPSCs can be induced to differentiate into a variety of specialized cell types. In addition, because iPSCs can be derived from a patient’s own cells, they offer the advantage of potentially reducing the risk of immune rejection and enabling patient-specific, autologous therapies [
40,
41].
Despite these advantages, iPSCs are associated with significant safety risks, including tumorigenicity and immunogenicity. Tumorigenicity concerns largely arise from the cell population heterogeneity. After reprogramming and cell expansion, iPSC lines often consist of a mixture of fully reprogrammed pluripotent cells, residual original specialized cells, and partially reprogrammed intermediates. Additionally, iPSCs tend to accumulate genetic changes, including chromosomal abnormalities, gene copy number variations, and single nucleotide polymorphisms, which may enhance tumor-forming potential [
42]. Various strategies have been explored to mitigate the tumorigenicity risks, including optimizing reprogramming methods, eliminating teratoma-forming cells via inducible cell suicide systems, and maximizing cell line purity through advanced cell sorting techniques [
42].
Autologous iPSCs are often assumed to be immunologically compatible. However, evidence indicates that some cells differentiated from autologous iPSCs can trigger a cytotoxic T cell-mediated immune response. This response is linked to the aberrant expression of specific genes, including Zg16 (a mediator of protein transport and carbohydrate binding) and Hormad1 (a meiotic regulator and DNA mismatch repair inhibitor in cancer) [
43-
45]. To improve the immune tolerance of iPSCs, several approaches are under investigation, including human leukocyte antigen knockout, cytotoxic response modulation, and cotransplantation with immunomodulatory MSCs [
45].
Taken together, while ESCs and iPSCs remain highly promising for regenerative medicine, their ethical, legal, and safety limitations preclude their immediate use in clinical applications for kidney diseases. At present, the most feasible strategy appears to involve autologous kidney progenitors and MSCs for cell therapies and for seeding bioengineered kidney constructs.
2. Translational Status
The clinical translation of novel regenerative medicine strategies is progressing at an unequal pace (summarized in
Table 1), largely reflecting specific challenges faced by individual approaches. Most clinical trials focus on MSC-based interventions, consistent with the overall enthusiasm for the MSC field. At the time of writing, a total of 53 studies involving MSC-based treatments for kidney diseases are registered in the ClinicalTrials.gov database (
Table 1). These studies span the translational spectrum, ranging from early safety evaluations (phase 1) to later-stage efficacy trials (phase 3), and employ diverse MSC sources, including bone marrow, adipose, and umbilical MSCs.
In contrast, cell-based therapies involving native kidney progenitors have not yet reached advanced stages of clinical translation. This limited progress is due to the outstanding technical difficulties of isolating and expanding such progenitors, coupled with gaps in understanding their underlying biology.
Pharmacological approaches aimed at promoting the endogenous kidney repair have shown more tangible advances. As described above, IL11 inhibition has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy for both acute and CKD. A phase I clinical trial [
27] was launched in 2022 to evaluate the safety profile and preliminary efficacy of anti-IL11 antibody therapy in human patients.
Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors also demonstrated potential for treating kidney diseases by correcting pathological epigenetic abnormalities in a number of preclinical studies [
27]. Several HDAC inhibitors are currently under investigation for the treatment of both kidney conditions and other indications, including cancer. One of them, valproic acid—a drug already approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration to treat seizures—has advanced to phase 2/3 testing for idiopathic glomerulosclerosis and minimal change disease.
Meanwhile, bioengineering strategies aimed at manufacturing functional replacement kidneys, although under active development, largely remain at a preclinical stage due to outstanding challenges associated with cell expansion, scale-up, and manufacturing. Approaches involving decellularized kidney ECM scaffolds are still undergoing optimization of cell removal and cell seeding protocols, ensuring the preservation of bioactive cues and overcoming the technical barriers of revascularization, tubule epithelium reconstruction, and repopulation of interstitial compartments. Scaling these processes to the size of an adult human kidney remains particularly challenging [
46]
CONCLUSIONS
Regenerative medicine has emerged as a promising response to the unmet clinical need in kidney disease treatment, with multiple strategies under active investigation. One approach focuses on enhancing the kidney’s limited intrinsic regenerative capacity by redirecting the injury response away from maladaptive repair pathways. This strategy has been enabled by recent advances in understanding the molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying kidney injury and repair. Several pharmacological interventions have been proposed to mitigate postinjury fibrosis and promote cellular recovery. A second major strategy involves stem cell-based therapies, supported by the identification of renal progenitor cell populations and growing insights into the renoprotective, immunomodulatory, and proregenerative paracrine effects of MSCs. Collectively, these efforts lay the groundwork for biologically informed therapies that move beyond symptomatic treatment toward true kidney regeneration.
NOTES
-
Funding/Support
This study received no specific grant from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
-
Conflict of Interest
The authors have nothing to disclose.
-
Author Contribution
Conceptualization: VM, JHK; Data curation: VM; Formal analysis: VM; Funding acquisition: NA; Methodology: NA; Project administration: JHK; Visualization: VM; Writing - original draft: VM, JHK; Writing - review & editing: VM, JHK.
Fig. 1.Summary diagram of pathogenic events in the injured kidney.
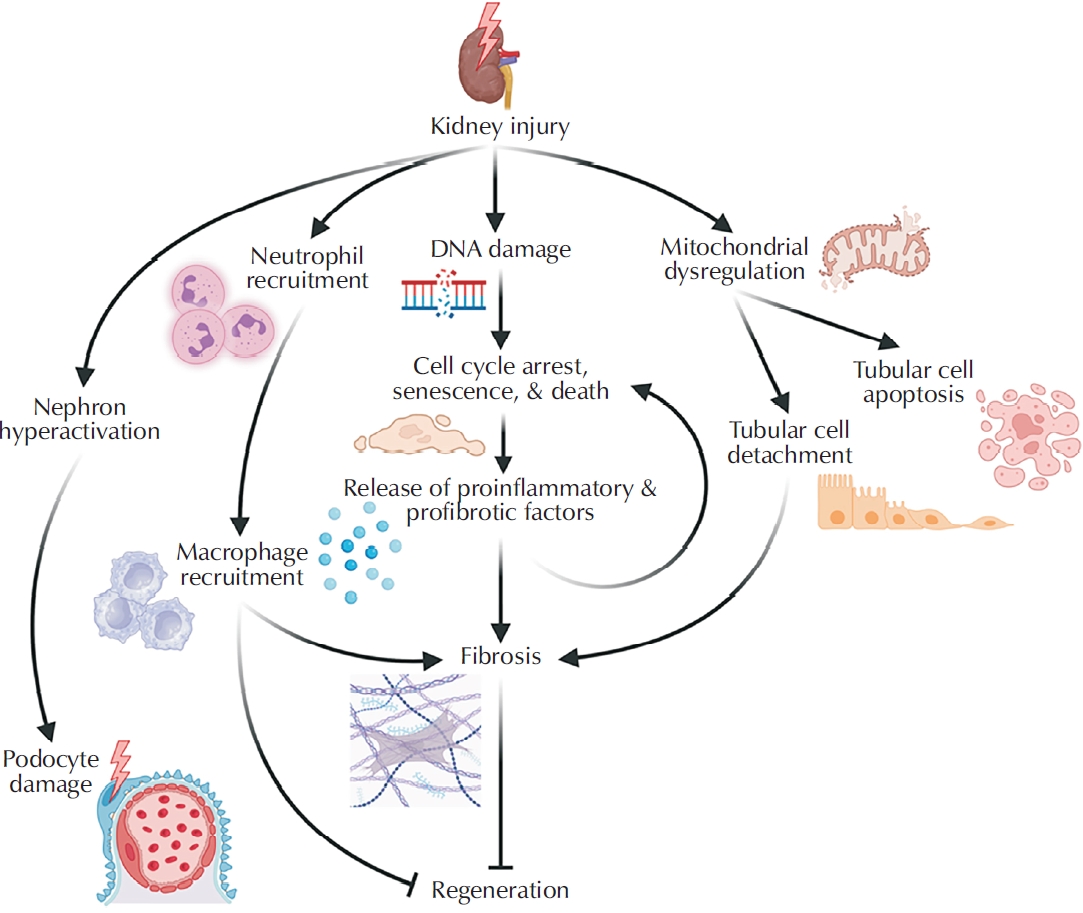
Fig. 2.Known kidney progenitor cells and their differentiation pathways. (A) Sox9-expressing tubular epithelial progenitors. (B) Protrudin (Zfyve27)-expressing tubular epithelial progenitors in the collecting duct epithelia and interstitial spaces of the renal papilla. (C) Pax2+ tubule epithelial cells progenitors. (D) CD133+CD24+ bipotent progenitors located at the urinary pole of the Bowman capsule and give rise to podocytes and epithelial cells of proximal tubules. (E) Extraglomerular renin-positive progenitors capable of giving rise to podocytes, mesangial cells, and glomerular parietal cells.
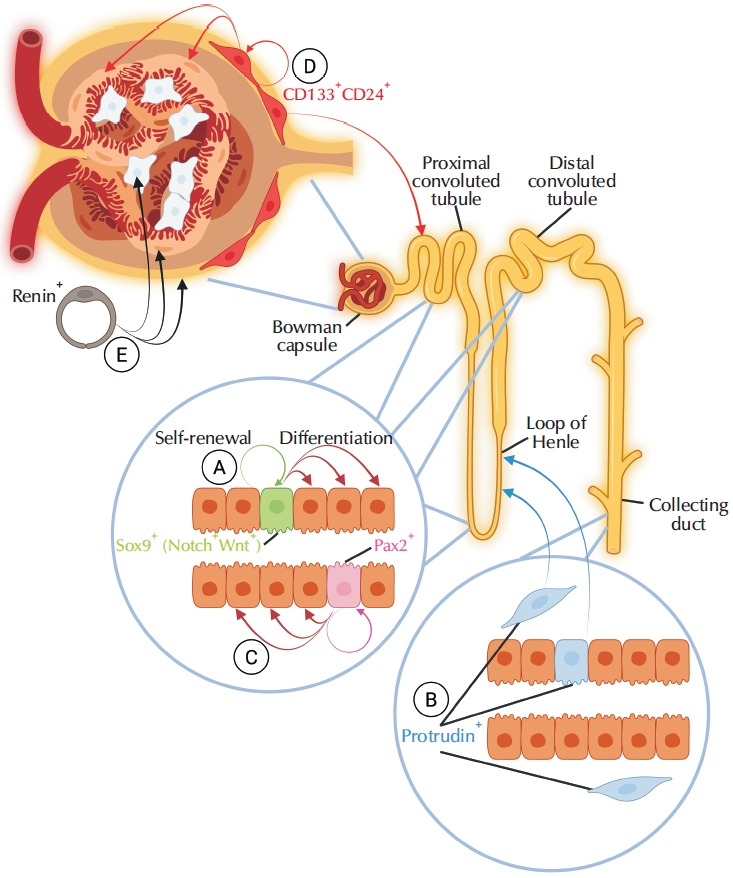
Table 1.Translational status of regenerative medicine-based therapeutic approaches
|
Therapy category |
Approach |
Clinical translation |
ClinicalTrials. gov ID |
Notes |
|
Facilitation of intrinsic regeneration |
IL11 inhibition |
Phase 1 completed |
NCT05658107 |
Evaluation of safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of an anti-IL11 antibodies in healthy male subjects |
|
Trichostatin A (HDAC inhibitor) |
Phase 1 ongoing |
NCT03838926 |
Safety study for another indication — relapses or refractory hematologic malignancies |
|
4-Phenylbutyrate (HDAC inhibitor) |
Phase 2/3 completed |
NCT02343094 |
Efficacy evaluation |
|
Valproic acid (HDAC inhibitor) |
Phase 2/3 completion status unknown |
NCT02896270 |
Efficacy study for idiopathic nephrotic syndrome treatment |
|
Kidney progenitor cells |
Sox9+ renal tubule cells progenitors |
None |
|
|
|
Protrudin (Zfyve27)+ tubule cell progenitors |
None |
|
|
|
Pax2+ tubule cell progenitors |
None |
|
|
|
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs)*
|
Injection of Wharton’s jelly-derived MSCs into the renal parenchyma |
Phase 1/2 completion status unknown |
NCT03288571 |
Safety evaluation in patients diagnosed with diabetic nephropathy |
|
Intravenously delivered allogeneic adipose-derived MSCs |
Phase 1 completed |
NCT05362786 |
Safety and tolerability |
|
Bone marrow-derived MSC-based therapy to treat diabetic kidney disease |
Phase 2 completed |
NCT07039318 |
Efficacy evaluation |
|
Umbilical cord MSCs in the treatment of Alport syndrome |
Phase 2/3 not yet recruiting |
NCT06731192 |
Safety and efficacy evaluation |
|
Organ replacement via tissue engineering |
Neo-kidney implant composed of autologous renal cells formulated in gelatin-based hydrogel in treatment of chronic kidney disease |
Phase 1 terminated, lack of funding |
NCT01846715 |
Safety evaluation |
REFERENCES
- 1. Ostermann M, Lumlertgul N, Jeong R, See E, Joannidis M, James M. Acute kidney injury. Lancet 2025;405:241-56.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Cockwell P, Fisher LA. The global burden of chronic kidney disease. Lancet 2020;395:662-64.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Vanholder R, Annemans L, Bello AK, Bikbov B, Gallego D, Gansevoort RT, et al. Fighting the unbearable lightness of neglecting kidney health: the decade of the kidney. Clin Kidney J 2021;14:1719-30.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 4. Widjaja AA, Viswanathan S, Shekeran SG, Adami E, Lim WW, Chothani S, et al. Targeting endogenous kidney regeneration using anti-IL11 therapy in acute and chronic models of kidney disease. Nat Commun 2022;13:7497.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 5. Maringhini S, Zoccali C. Chronic kidney disease progression-a challenge. Biomedicines 2024;12:2203.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Moon KH, Ko IK, Yoo JJ, Atala A. Kidney diseases and tissue engineering. Methods 2016;99:112-9.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Rayego-Mateos S; Marquez-Expósito L, Rodrigues-Diez R, Sanz AB, Guiteras R, Doladé N, et al. Molecular mechanisms of kidney injury and repair. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23:1542.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Corridon PR, Ko IK, Yoo JJ, Atala A. Bioartificial kidneys. Curr Stem Cell Rep 2017;3:68-76.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 9. Elliott DA. Hemodialysis. Clin Tech Small Anim Pract 2000;15:136-48.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Basile C, Davenport A, Mitra S, Pal A, Stamatialis D, Chrysochou C, et al. Frontiers in hemodialysis: innovations and technological advances. Artif Organs 2021;45:175-82.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 11. Nalesso F, Garzotto F, Cattarin L, Bettin E, Cacciapuoti M, Silvestre C. The future for end-stage kidney disease treatment: Implantable bioartificial kidney challenge. Appl Sci 2024;14:491.Article
- 12. Chung HC, Ko IK, Atala A, Yoo JJ. Cell-based therapy for kidney disease. Korean J Urol 2015;56:412-21.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Lentine KL, Pastan S, Mohan S, Reese PP, Leichtman A, Delmonico FL, et al. A roadmap for innovation to advance transplant access and outcomes: a position statement from the National Kidney Foundation. Am J Kidney Dis 2021;78:319-32.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Zambon JP, Magalhaes RS, Ko I, Ross CL, Orlando G, Peloso A, et al. Kidney regeneration: where we are and future perspectives. World J Nephrol 2014;3:24-30.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. Chapman JR. What are the key challenges we face in kidney transplantation today? Transplant Res 2013;2(Suppl 1):S1.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 16. Schnaper HW. Remnant nephron physiology and the progression of chronic kidney disease. Pediatr Nephrol 2014;29:193-202.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Balzer MS, Rohacs T, Susztak K. How many cell types are in the kidney and what do they do? Annu Rev Physiol 2022;84:507-31.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Thomasova D, Anders HJ. Cell cycle control in the kidney. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2015;30:1622-30.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Shankland SJ, Freedman BS, Pippin JW. Can podocytes be regenerated in adults? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 2017;26:154-64.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 20. Pippin JW, Kaverina NV, Eng DG, Krofft RD, Glenn ST, Duffield JS, et al. Cells of renin lineage are adult pluripotent progenitors in experimental glomerular disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2015;309:F341-58.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Perico L, Morigi M, Rota C, Breno M, Mele C, Noris M, et al. Human mesenchymal stromal cells transplanted into mice stimulate renal tubular cells and enhance mitochondrial function. Nat Commun 2017;8:983.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 22. Forbes JM, Hewitson TD, Becker GJ, Jones CL. Ischemic acute renal failure: long-term histology of cell and matrix changes in the rat. Kidney Int 2000;57:2375-85.ArticlePubMed
- 23. Lazzeri E, Angelotti ML, Peired A, Conte C, Marschner JA, Maggi L, et al. Endocycle-related tubular cell hypertrophy and progenitor proliferation recover renal function after acute kidney injury. Nat Commun 2018;9:1344.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 24. Shirane M. Roles of protrudin at interorganelle membrane contact sites. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci 2019;95:312-20.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Davies JA, Murray P, Wilm B. Regenerative medicine therapies: lessons from the kidney. Curr Opin Physiol 2020;14:41-7.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Rastaldi MP, Ferrario F, Giardino L; Dell'Antonio G, Grillo C, Grillo P, et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition of tubular epithelial cells in human renal biopsies. Kidney Int 2002;62:137-46.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Ingelheim B. A study to test how different doses of BI 765423 are taken up in the body of healthy men 2024 [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): ClinicalTrials.gov; 2024 [2025 May 4]. Available from: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05658107
- 28. Kumar S, Liu J, Pang P, Krautzberger AM, Reginensi A, Akiyama H, et al. Sox9 activation highlights a cellular pathway of renal repair in the acutely injured mammalian kidney. Cell Rep 2015;12:1325-38.ArticlePubMed
- 29. Kang HM, Huang S, Reidy K, Han SH, Chinga F, Susztak K. Sox9-positive progenitor cells play a key role in renal tubule epithelial regeneration in mice. Cell Rep 2016;14:861-71.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Zhang W, Gao C, Tsilosani A, Samarakoon R, Plews R, Higgins PJ. Potential renal stem/progenitor cells identified by in vivo lineage tracing. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2022;322:F379-91.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 31. Oliver JA, Sampogna RV, Jalal S, Zhang QY, Dahan A, Wang W, et al. A subpopulation of label-retaining cells of the kidney papilla regenerates injured kidney medullary tubules. Stem Cell Reports 2016;6:757-71.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 32. Ronconi E, Sagrinati C, Angelotti ML, Lazzeri E, Mazzinghi B, Ballerini L, et al. Regeneration of glomerular podocytes by human renal progenitors. J Am Soc Nephrol 2009;20:322-32.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 33. Barker N, Rookmaaker MB, Kujala P, Ng A, Leushacke M, Snippert H, et al. Lgr5(+ve) stem/progenitor cells contribute to nephron formation during kidney development. Cell Rep 2012;2:540-52.ArticlePubMed
- 34. García-Bernal D; García-Arranz M; Yáñez RM; Hervás-Salcedo R, Cortés A; Fernández-García M, et al. The current status of mesenchymal stromal cells: controversies, unresolved issues and some promising solutions to improve their therapeutic efficacy. Front Cell Dev Biol 2021;9:650664.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Horwitz EM, Le Blanc K, Dominici M, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini FC, et al. Clarification of the nomenclature for MSC: the International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2005;7:393-5.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I, Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006;8:315-7.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Viswanathan S, Shi Y, Galipeau J, Krampera M, Leblanc K, Martin I, et al. Mesenchymal stem versus stromal cells: International Society for Cell & Gene Therapy (ISCT®) mesenchymal stromal cell committee position statement on nomenclature. Cytotherapy 2019;21:1019-24.ArticlePubMed
- 38. Huang Y, Yang L. Mesenchymal stem cells and extracellular vesicles in therapy against kidney diseases. Stem Cell Res Ther 2021;12:219.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 39. Torabinavid P, Khosropanah MH, Azimzadeh A, Kajbafzadeh AM. Current strategies on kidney regeneration using tissue engineering approaches: a systematic review. BMC Nephrol 2025;26:66.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 40. Park SJ, Kim YY, Han JY, Kim SW, Kim H, Ku SY. Advancements in human embryonic stem cell research: clinical applications and ethical issues. Tissue Eng Regen Med 2024;21:379-94.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 41. Eguizabal C, Aran B; Chuva de Sousa Lopes SM, Geens M, Heindryckx B, Panula S, et al. Two decades of embryonic stem cells: a historical overview. Hum Reprod Open 2019;2019:hoy024.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 42. Zhong C, Liu M, Pan X, Zhu H. Tumorigenicity risk of iPSCs in vivo: nip it in the bud. Precis Clin Med 2022;5:pbac004.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 43. Zhao T, Zhang ZN, Rong Z, Xu Y. Immunogenicity of induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 2011;474:212-5.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 44. Liu K, Wang Y, Zhu Q, Li P, Chen J, Tang Z, et al. Aberrantly expressed HORMAD1 disrupts nuclear localization of MCM8-MCM9 complex and compromises DNA mismatch repair in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis 2020;11:519.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 45. Hong Z, Zhao Y, Pahlavan S, Wang X, Han S, Wang X, et al. iPSC modification strategies to induce immune tolerance. Life Med 2025;4:lnaf016.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 46. Little MH, Rabelink TJ. Replacing renal function using bioengineered tissues. Nat Rev Bioeng 2023;1:576-88.ArticlePDF
 , Ji Hyun Kim
, Ji Hyun Kim



 KAUTII
KAUTII

 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite