-
Primary Bladder and Ureteral Amyloidosis Initially Diagnosed as Chronic Cystitis: A Case Report
-
Seungsoo Lee, Dan Bee Lee, Hyun Jung Lee, Won Hoon Song, Sung-Woo Park, Jong Kil Nam
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):167-172. Published online December 31, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550038019
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
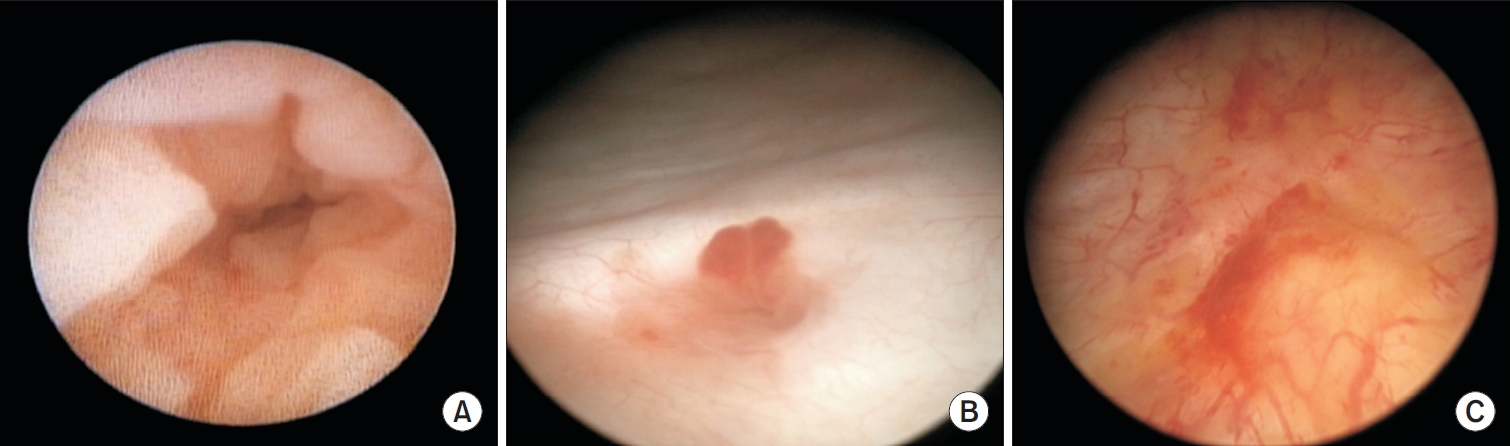
- Primary localized amyloidosis confined to the urinary tract is uncommon and frequently misinterpreted due to clinical and radiologic overlap with more prevalent conditions. We describe a 69-year-old woman who experienced recurrent gross hematuria over 2 years and underwent initial transurethral resection based on a presumptive diagnosis of chronic cystitis. Subsequent evaluation revealed a left ureteral mass with hydronephrosis, raising concern for malignancy. Histopathologic examination of both bladder and ureteral specimens demonstrated amorphous eosinophilic deposits that stained positive with Congo red and showed apple-green birefringence under polarized microscopy. Immunofluorescence confirmed λ-light-chain predominance, establishing AL (amyloid light chain)-type amyloidosis without systemic involvement. The patient underwent complete endoscopic resection and remains asymptomatic during ongoing surveillance. This case highlights the diagnostic challenges posed by localized urinary amyloidosis and underscores the importance of histologic confirmation in atypical inflammatory lesions.
-
Clinical Guideline of Genital Herpes Virus Infection
-
Jong Kil Nam, Sang Don Lee
-
Korean J Urogenit Tract Infect Inflamm 2010;5(1):18-26. Published online April 30, 2010
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Genital herpes is one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases, While genital herpes can present with self limiting genital lesions. Many such persons have mild or unrecognized infections but shed virus intermittently in the genital tract. It is incurable and persists during the lifetime of the host, often in latent form. Treatment can be expected to reduce the formation of new lesions, the duration of pain, the time required for healing and antiviral shedding. However, antiviral agents do not cure Human simplex virus infections, but rather offer clinical benefits to the majority of symptomatic patients and is the mainstay of management. Our review is to summarize the treatment and management of genital herpes, which is to help patients deal with the infection and be prevented from sexual and perinatal transmission.
|