Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Efficacy of Urovaxom for Improving Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome Symptoms in Prostate Cancer Patients Who Underwent Radical Prostatectomy: A Multicenter, Prospective Cohort Study
- Jun-Koo Kang, Yun-Sok Ha, Sungchan Park, Tae Gyun Kwon, Tae-Hwan Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):42-47. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550014007
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS) is a multifactorial condition that can significantly diminish quality of life. Although some patients have reported persistent pelvic pain after radical prostatectomy (RP), the prevalence and direct causal relationship between CPPS and RP remain unclear. This multicenter prospective study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of Urovaxom for improving CPPS symptoms. Materials and Methods: A total of 52 prostate cancer patients who underwent RP were enrolled and administered Urovaxom (60 mg/day) for 12 weeks. Changes in National Institutes of Health Chronic Prostatitis Symptom Index (NIH-CPSI), overactive bladder symptom score (OABSS), International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS), and inflammation markers (white blood cell [WBC], C-reactive protein [CRP]) were analyzed using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test.
Results
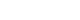
After 12 weeks of treatment, the NIH-CPSI total score significantly decreased from 19 (interquartile range [IQR], 16–23) to 12.5 (IQR, 8.0–16.8) (p<0.001). The OABSS total score decreased from 8 (IQR, 4–11) to 5 (IQR, 3.0–7.8), and the IPSS total score decreased from 13.5 (IQR, 10.0–22.8) to 10.5 (IQR, 5.0–17.0) (p<0.001). WBC levels showed a slight increase (p=0.028), but the clinical relevance of this change is uncertain and warrants further investigation. CRP changes were not statistically significant (p=0.274).
Conclusions
Urovaxom demonstrated significant efficacy in improving CPPS symptoms, particularly pain and reduced quality of life, in patients following RP. These findings suggest Urovaxom as a potential therapeutic option for CPPS after management using RP. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef - Addressing an Unmet Need in Postprostatectomy Care: Perspectives on Urovaxom
Byeong Jin Kang
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(2): 118. CrossRef
- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 4,757 View
- 42 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effect of Residual Stone Fragments on Patient-Reported Quality of Life after Endoscopic Kidney Stone Surgery
- Sang Hee Lee, Jun-Koo Kang, Jae-Wook Chung, Yun-Sok Ha, Jun Nyung Lee, Seock Hwan Choi, Hyun Tae Kim, Tae-Hwan Kim, Eun Sang Yoo, Tae Gyun Kwon, Bum Soo Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2024;19(2):31-39. Published online August 31, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2024.19.2.31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: This study examined the effects of residual fragments (RF) on the patient-reported quality of life (QOL) after kidney stone surgery, such as retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) and percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL), using the Korean version of the Wisconsin Stone Quality of Life Questionnaire (K-WISQOL).
Materials and Methods: The medical records of 156 patients who underwent RIRS or PCNL and completed the preoperative and postoperative K-WISQOL from January 2021 to September 2023 were analyzed retrospectively. The patients were divided into RIRS and PCNL groups by the surgical method. The participants completed the K-WISQOL within four weeks before and after treatment. The patients’ baseline characteristics, surgical outcomes, and K-WISQOL scores were compared according to the presence of RF in each surgical group.
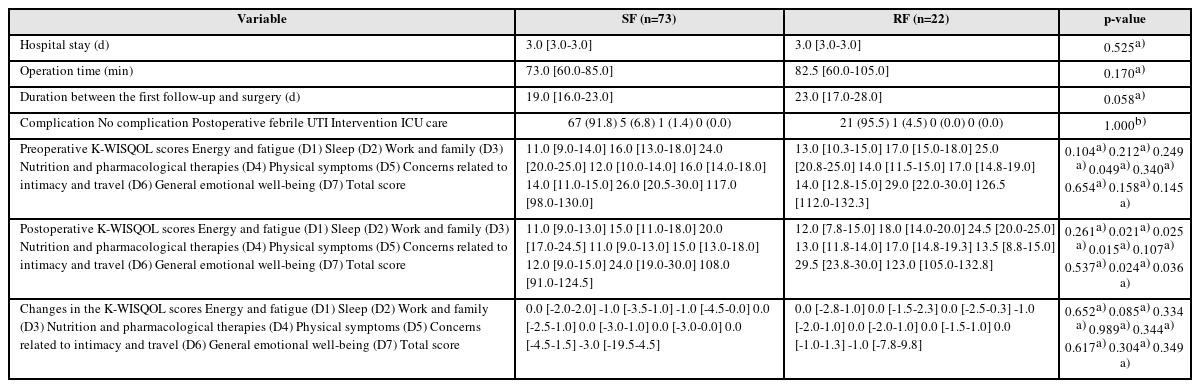
Results: Of the 156 patients, 95 underwent RIRS, and 61 underwent PCNL. In the RIRS group, the patients’ baseline characteristics and surgical outcomes were similar in the stone-free (SF) and RF subgroups. The changes in all K-WISQOL domain scores and total scores were similar in the two subgroups. In the PCNL group, the RF subgroup had a significantly higher proportion of staghorn stones, a significantly larger mean stone diameter and significantly longer operation time than those of the SF subgroup. But, the changes in all K-WISQOL domain scores and total scores were not significantly different between the two subgroups, as observed in the RIRS group.
Conclusions: This study showed that the presence of RFs after endoscopic kidney surgery did not affect the short-term patient-reported QOL regardless of the surgical methods.
- 3,284 View
- 39 Download


 KAUTII
KAUTII

 First
First Prev
Prev