Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors of Fournier Gangrene: A 15-Years Multicenter Retrospective Study in Korea
- Seung-Kwon Choi, Sin Woo Lee, Hyung-Lae Lee, Jeong Woo Lee, Jung Sik Huh, Yeonjoo Kim, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):159-166. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550036018
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose
Fournier gangrene (FG) is a rare but life-threatening necrotizing infection requiring prompt recognition and intervention. This multicenter study aimed to investigate the clinical characteristics, treatment outcomes including mortality, and risk factors associated with death among patients with FG over the past 15 years in Korea. Materials and Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 84 patients diagnosed with FG between 2008 and 2022 across 7 hospitals. Demographics, comorbidities, laboratory findings, and clinical outcomes were analyzed. Mortality-related risk factors were assessed using univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Results
The mean age was 58.1±15.9 years, and 95.2% of patients were male. Diabetes mellitus (42.9%) and hypertension (36.9%) were the most prevalent comorbidities. Sepsis developed in 38.1% of patients, and the overall mortality rate was 14.3%. In univariate analysis, age ≥70 years, low body mass index, diabetes mellitus, low hemoglobin, low hematocrit, high respiratory rate, and Fournier gangrene severity index (FGSI) ≥9 were significantly associated with mortality. After data correction and multivariate adjustment, diabetes mellitus (odds ratio [OR], 39.61; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.39–656.32; p=0.010) and respiratory rate (OR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.09–1.91; p=0.011) were identified as independent predictors of mortality. FGSI≥9 demonstrated borderline association with mortality (p=0.08), indicating its potential clinical relevance.
Conclusions
In this multicenter Korean cohort, the mortality rate of FG remained substantial at 14.3%. Diabetes mellitus and elevated respiratory rate were independent predictors of mortality, while FGSI≥9 demonstrated a borderline yet clinically meaningful association, suggesting its role as a useful severity indicator in early risk stratification.
- 247 View
- 9 Download

Case Report
- Hemangioma Mistaken for Renal Cell Carcinoma in a Patient With End-Stage Renal Disease: A Case Report
- Hyung-Lae Lee, Dong-Gi Lee, Jeong Woo Lee, Jeonghyouk Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(1):48-51. Published online April 30, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550008004
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
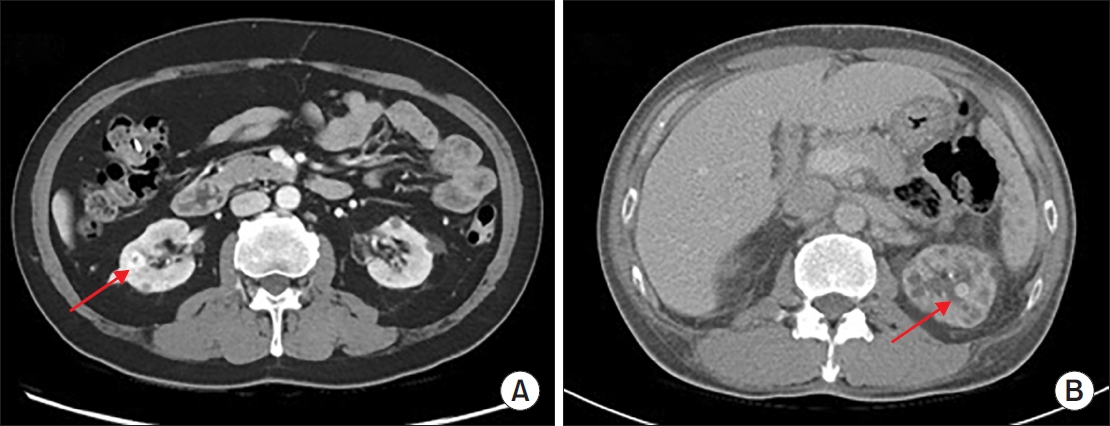
ePub - Hemangiomas are rare, benign vascular neoplasms that are more common in patients with end-stage renal disease. Here, we describe 2 cases of hemangioma misdiagnosed as renal cell carcinoma before renal transplantation. The key finding in our case was the misdiagnosis of hemangiomas as renal cell carcinoma based on computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in patients with end-stage renal disease. Because living transplantation was planned for our patients, we performed rapid surgical resection of the heterogeneously enhancing renal masses to avoid delays in transplantation. Our case highlights the importance of rapid surgical resection of enhanced renal masses to confirm diagnosis, thereby avoiding delays in patients scheduled for renal transplantation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(1): 1. CrossRef
- Editorial for UTI 2025 Vol. 20 No. 1 - Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
- 1,809 View
- 18 Download
- 1 Crossref

Original Article
- Risk Factors for Sepsis after Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery: Single Center Experience
- Jinseok Kang, Koo Han Yoo, Taesoo Choi, Gyeong Eun Min, Dong-Gi Lee, Hyung-Lae Lee, Jeonghyouk Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):93-100. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.93
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: To evaluate risk factors for sepsis after retrograde intrarenal surgery for treatment of renal stones.
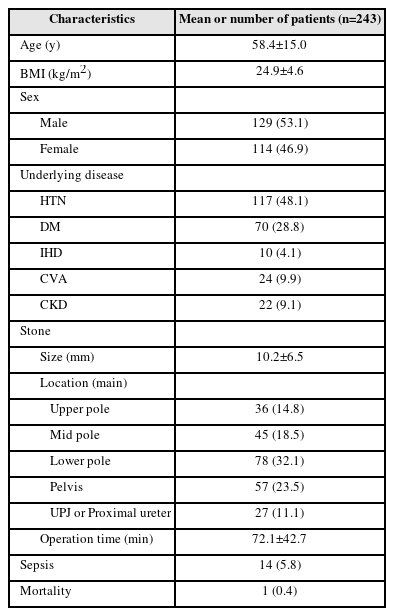
Materials and Methods: We analyzed the clinical data of 243 patients with kidney stones who visited our institution between April 2017 and April 2023. Age, sex, body mass index, underlying disease, location and size of stones, previous history of stones, previous history of urinary tract infections, duration of surgery, preoperative drainage, application of ureteral balloon dilation, and laboratory test results were included in the analysis.
Results: The mean age of the patients was 58.4 (±15.0) years; there were more men (53.1%) than women (46.9%). Of the 243 patients, the overall rate of sepsis was 5.8% (n=14) and the total mortality rate was 0.4% (n=1). In univariate analysis, history of urinary tract infection (p=0.019), positive preoperative urine culture test (p=0.009), operative duration of more than 90 min (p=0.004), and application of ureter balloon dilation (p=0.016) were statistically significant. In multivariate analysis, positive finding in the urine culture test performed before surgery (p=0.003), operation duration >90 min (p=0.005), and use of balloon dilation during surgery (p=0.011) were statistically significant.
Conclusions: There is a risk of progression to postoperative sepsis if bacteria are detected in the urine culture before surgery, if the operative time exceeds 90 min, or if balloon dilation is performed during surgery. Given that the probability of progression to sepsis is approximately 6%, close observation and active treatment are needed for patients with these risk factors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Establishing an AI-based artifact correction system for intrarenal pressure monitoring using the LithoVue™ Elite ureteroscope: an EAU endourology and AUSET collaboration
Takahiro Yanase, Shuzo Hamamoto, Rei Unno, Steffi Kar Kei Yuen, Vineet Gauhar, Bhaskar K. Somani, Olivier Traxer, Yuya Sasaki, Ryosuke Chaya, Atsushi Okada, Kazumi Taguchi, Takahiro Yasui
World Journal of Urology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of postoperative infection factors of retrograde intrarenal surgery combined with negative pressure equipment for renal stones
Deheng Cui, Qinghong Ma, Qiuyan Zhang, Lian Zhang, Guoqiang Chen
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Establishing an AI-based artifact correction system for intrarenal pressure monitoring using the LithoVue™ Elite ureteroscope: an EAU endourology and AUSET collaboration
- 4,819 View
- 88 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KAUTII
KAUTII

 First
First Prev
Prev