Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review Article
- Adult Syphilis: A Narrative Review of Clinical Insights and Public Health Implications in Urology
- Seung-Ju Lee, Jin Bong Choi
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):123-131. Published online December 31, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550039017
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
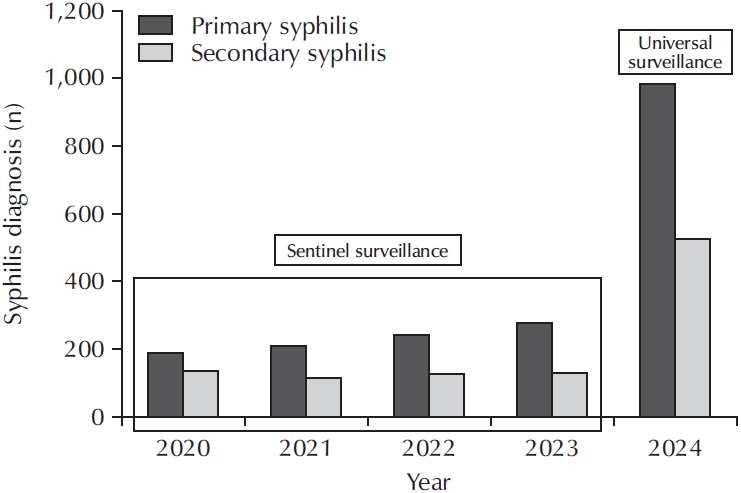
ePub - Syphilis continues to pose a major global public health concern, with more than 7 million cases reported worldwide in 2022, and its incidence continues to rise in numerous regions. In Korea, the shift from sentinel to universal notification in 2024 has revealed a markedly greater disease burden, particularly among men who have sex with men and among younger adults, underscoring changing epidemiological patterns and the urgent need for revised control strategies. In urological practice, syphilis presents with a wide range of often misleading symptoms, including painless genital ulcers, urethritis, and sexual dysfunction, that frequently resemble other genitourinary disorders and complicate diagnostic evaluation. Accurate identification relies on integrating a thorough clinical assessment with serologic testing while remaining alert to diagnostic challenges such as early latent infection, serofast states, and human immunodeficiency virus coinfection. Penicillin G remains the mainstay of therapy, with treatment regimens tailored to the stage of disease and to the presence or absence of central nervous system involvement. Effective partner notification, targeted screening, and consistent follow-up are essential to prevent reinfection and limit further transmission. At a public health level, a multifaceted strategy—strengthened surveillance systems, focused testing in high-risk populations, and embedding syphilis screening within broader sexually transmitted infection care frameworks—is critical to curbing its resurgence. In summary, prompt recognition, adherence to evidence-based management, and coordinated public health measures, together with ongoing advances in diagnostics and prevention, remain fundamental to reducing the continued spread of syphilis and mitigating its impact on both individual and population health.
- 321 View
- 6 Download

Original Article
- Trends in Age-Specific Prevalence of Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
- Young Hwan Kim, Se Hwa Hong, Tae Wook Kang, Hyun Chul Chung, Tae Hyoung Kim, Sae Chul Kim, Sang Baek Koh, Jae Hung Jung
- Urogenit Tract Infect 2023;18(3):101-106. Published online December 31, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2023.18.3.101
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Purpose: To elucidate the longitudinal changes in the prevalence of lower urinary tract dysfunction (LUTD) according to age over the past 10 years.
Materials and Methods: The changes in the proportion of prevalence for LUTD, including benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and urinary incontinence (UI) among South Koreans from 2009 to 2018, were analyzed using the National Health Information Database established by the Korean National Health Insurance Service. All conditions were defined according to the corresponding Korean Standard Classification of Diseases-8 for diagnosis and surgical procedures and Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service codes for drugs.
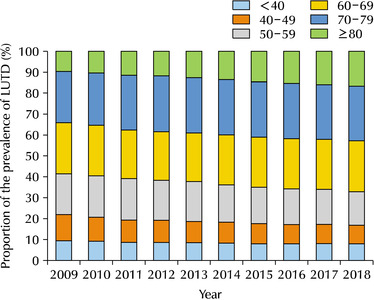
Results: The 60-69, 70-79, and over 80 age groups accounted for more than 60% of the LUTD cases from 2009 to 2018, while significant increases in the crude prevalence of LUTD were observed over a 10-year period in all age groups (p for trend <0.05). In age groups over 60 years, LUTD was more prevalent in men than women, but there was no statistically significant difference in proportion (p>0.05). The changes in the prevalence and prevalence proportion exhibited similar trends in BPH, UI, and LUTD.
Conclusions: LUTD was more prevalent in the elderly aged over 60 years old than in younger adults. Therefore, this study suggests the development of nationwide healthcare policies to manage LUTD in the elderly population of South Korea, which is expected to become the world’s most aged population.
- 4,292 View
- 20 Download


 KAUTII
KAUTII
 First
First Prev
Prev