-
Beta-Lactamase-Mediated Antibiotic Resistance in Urinary Tract Infections: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies
-
Fanglin Shao, Dengxiong Li, Jie Wang, Zhouting Tuo, Zhipeng Wang, Wuran Wei, Ruicheng Wu, Dechao Feng
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(2):67-81. Published online August 31, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550012006
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader
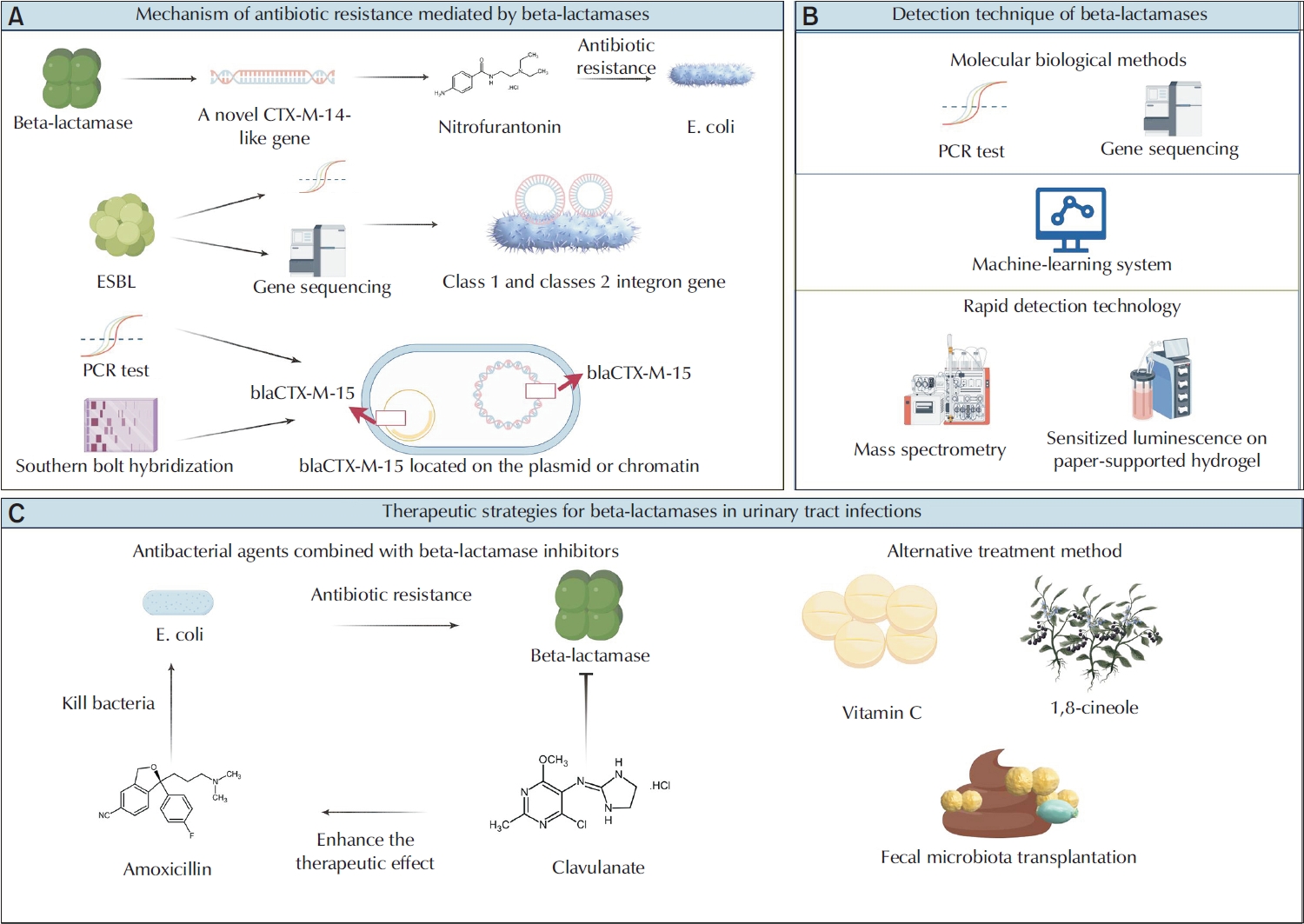
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are among the most prevalent bacterial infections globally, and are primarily caused by Escherichia and Klebsiella. The overprescription and inappropriate use of antibiotics have accelerated the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria. Beta-lactamases play a critical role in mediating antibiotic resistance in UTIs. These enzymes promote bacterial resistance through multiple mechanisms, including gene mutation, plasmid-mediated horizontal gene transfer, and the involvement of integrons. Comprehensive knowledge of the ways in which beta-lactamases contribute to resistance in UTIs is essential for improving treatment strategies. Advances in detection technologies, such as gene sequencing and mass spectrometry, have greatly enhanced the ability to monitor and predict bacterial resistance. Current therapeutic strategies include the application of beta-lactamase inhibitors, the development of novel antibiotics, and alternative treatments that have shown efficacy against beta-lactamase-mediated antibiotic resistance. This paper reviews the mechanisms of beta-lactamase-mediated resistance in UTIs and provides an in-depth overview of several detection methods and therapeutic approaches.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Editorial for Urogenital Tract Infection (UTI) 2025 Vol. 20 No. 2 – Highlights of This Issue’s Papers and the UTI Editors’ Pick
Koo Han Yoo
Urogenital Tract Infection.2025; 20(2): 55. CrossRef
-
4,805
View
-
58
Download
-
1
Crossref
|