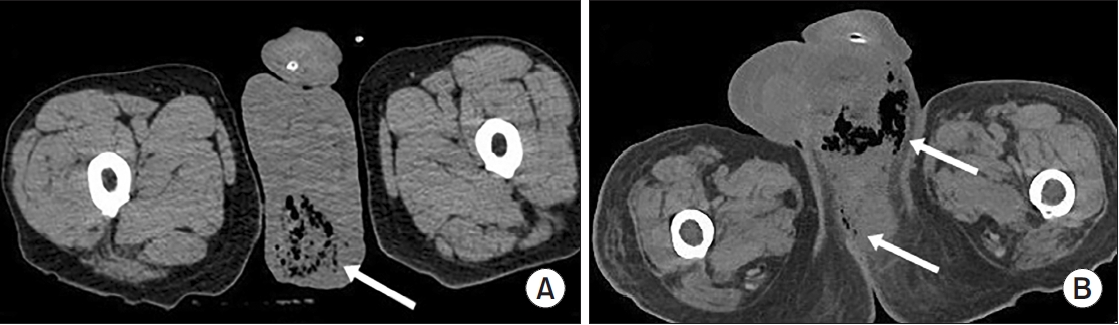
-
Clinical Characteristics and Risk Factors of Fournier Gangrene: A 15-Years Multicenter Retrospective Study in Korea
-
Seung-Kwon Choi, Sin Woo Lee, Hyung-Lae Lee, Jeong Woo Lee, Jung Sik Huh, Yeonjoo Kim, Sangrak Bae, Tae-Hyoung Kim
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2025;20(3):159-166. Published online December 31, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2550036018
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Purpose
Fournier gangrene (FG) is a rare but life-threatening necrotizing infection requiring prompt recognition and intervention. This multicenter study aimed to investigate the clinical characteristics, treatment outcomes including mortality, and risk factors associated with death among patients with FG over the past 15 years in Korea.
Materials and Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 84 patients diagnosed with FG between 2008 and 2022 across 7 hospitals. Demographics, comorbidities, laboratory findings, and clinical outcomes were analyzed. Mortality-related risk factors were assessed using univariate and multivariate logistic regression analysis.
Results
The mean age was 58.1±15.9 years, and 95.2% of patients were male. Diabetes mellitus (42.9%) and hypertension (36.9%) were the most prevalent comorbidities. Sepsis developed in 38.1% of patients, and the overall mortality rate was 14.3%. In univariate analysis, age ≥70 years, low body mass index, diabetes mellitus, low hemoglobin, low hematocrit, high respiratory rate, and Fournier gangrene severity index (FGSI) ≥9 were significantly associated with mortality. After data correction and multivariate adjustment, diabetes mellitus (odds ratio [OR], 39.61; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.39–656.32; p=0.010) and respiratory rate (OR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.09–1.91; p=0.011) were identified as independent predictors of mortality. FGSI≥9 demonstrated borderline association with mortality (p=0.08), indicating its potential clinical relevance.
Conclusions
In this multicenter Korean cohort, the mortality rate of FG remained substantial at 14.3%. Diabetes mellitus and elevated respiratory rate were independent predictors of mortality, while FGSI≥9 demonstrated a borderline yet clinically meaningful association, suggesting its role as a useful severity indicator in early risk stratification.
-
The Risk Factors of Recurrent Febrile Urinary Tract Infection within 1 Year in Urinary Stone Patients with Acute Obstructive Pyelonephritis
-
Sin Woo Lee, Sol Yoon, Jungmo Do, Deok Ha Seo, Chunwoo Lee, Seong Uk Jeh, See Min Choi, Sung Chul Kam, Jeong Seok Hwa, Ky Hyun Chung, Jae Seog Hyun
-
Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(2):82-88. Published online August 31, 2017
-
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF
- Purpose: To identify and evaluate the risk factors for the development of recurrent febrile urinary tract infection (fUTI) among patients with previous urinary stone and acute obstructive pyelonephritis (OPN).
Materials and Methods: We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 52 patients, who had urinary tract stones presented with OPN, between 2010 and 2015. Following their initial treatment, patients who were subsequently admitted with fUTI were included.
Results: The mean age of patients was 62.2±14.6 years, and the mean follow-up duration was 26.0±20.39 months. Escherichia coli was found to be the dominating organism (68.2%, 15/22) in the initial urine culture. Patients were divided into two groups: The recurrent fUTI group (n=23) and the non-recurrent fUTI group (n=29). Between these two groups, significant differences were found with respect to diabetes history (recurrent group: 47.8% vs. non-recurrent group; 17.2%, p=0.018), stone location (kidney, 60.9% vs. ureter, 31.0%, p=0.031), and initially positive urine culture (60.9% vs. 27.6%, p=0.016). In a multivariate analysis, having an initially positive urine culture (95% confidence interval, 1.130-224.117; p=0.040) was identified as being an independent risk factor for developing recurrent fUTI. In a multivariate analysis, the initial laboratory test finding of acute renal insufficiency (ARI, p=0.019) and presence of a kidney stone (p=0.022) were significant factors associated with a newly-diagnosed-positive urine culture diagnosis.
Conclusions: Having an initially positive urine culture was a significant risk factor for the development of recurrent fUTI in urinary stone patients with acute OPN. In addition, repeated urine tests were also needed in patients with ARI or renal stones during the follow-up period.
|